| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | May-09-24 | |
| Add internal links | Nisha | Feb-18-25 | |
| Add internal links | Nisha | Feb-18-25 |

- Blog
- bse case study
BSE Case Study: Business Model And SWOT Analysis
The Bombay Stock Exchange is a titan of Indian Finance. With a history stretching back to the 1800s, it is not just the oldest stock exchange in Asia, but a vital part of the country’s economic story. But how does the BSE stack up in today’s fast-paced financial world?
In this blog, we will explore the exchange’s rich past and analyse the risks and opportunities.
The Bombay Stock Exchange, or BSE, is a stock exchange located in Mumbai, India. Established in 1875, it is the oldest stock exchange in Asia and the tenth oldest in the world. It is one of the India’s leading exchange groups and is known as the ‘Dalal Street’ which is often regarded as the Wall Street of India.
It provides a platform for trading in equities, currencies, debt instruments, derivatives, and
BSE History
The story starts under a banyan tree near Mumbai Town Hall, where a handful of stockbrokers would gather to trade in the 1850s.
Premchand Roychand, a cotton merchant, is credited with formalising these informal gatherings by establishing the ‘Native Share and Stock Brokers Association in 1875. This is the official founding year of the BSE.
Owning to the rapid increase of brokers, the trading venue relocated multiple times in Mumbai before eventually establishing its permanent residence on Dalal Street.
By 1950, the BSE had grown significantly. In 1957, the Indian Government officially recognised it as the country’s first stock exchange, granting it official trading rights. Since then, BSE has continuously evolved to keep pace with the times.
BSE Business Model
The BSE operates on a transaction-based fee model, generating revenue from various activities. Below is an analysis of the fundamental components of the business model of the BSE:
Trading Platform
The BSE offers a platform for investors to buy and sell stocks, currencies, derivatives, and other financial instruments. This platform connects buyers and sellers efficiently and charge a fee for the same.
Price discovery
It facilitates price discovery and determines the fair market value of securities traded on the exchange through buy and sell orders.
Market Information
The BSE effectively disseminates real-time market data and information to investors, thereby facilitating their ability to make informed investment decisions. Furthermore, customer segments of the BSE include Retail & Institutional investors, brokers, and issuers.
It generates its revenue from the following:
Listing Fees – The Companies pay a fee to list their shares on the BSE. Further, many other parties, such as Asset Management Companies, Brokerage houses, etc. pay a fee for the membership.
Trading Fees – The exchange charges a fee for every buy and sell order executed on the platform. This can be a fixed amount or a percentage of the transaction value (turnover).
Read Also: CAMS Case Study: Business Model, KPIs, and SWOT Analysis
BSE Financial Statements
Let’s have a look at the financial statements of the exchange:
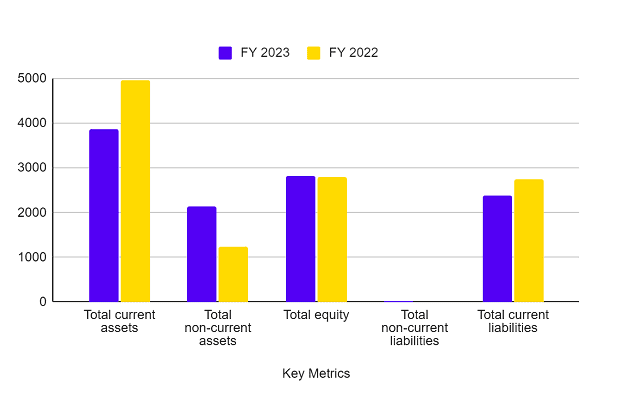
Balance Sheet
| Key Metrics | FY 2023 (INR crore) | FY 2022 (INR crore) |
|---|---|---|
| Total current Assets | 3,857.10 | 4,953.54 |
| Total non-current Assets | 2,136.71 | 1,231.86 |
| Total Equity | 2,828.99 | 2,789.71 |
| Total Non-current Liabilities | 14.49 | 10.87 |
| Total Current Liabilities | 2,392.69 | 2,743.93 |
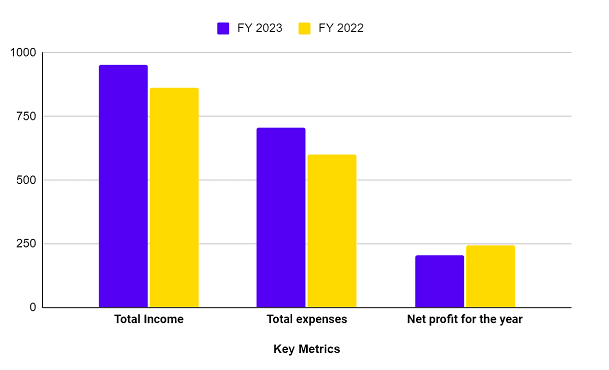
Income Statement
| Key Metrics | FY 2023 (INR crore) | FY 2022 (INR crore) |
|---|---|---|
| Total Income | 953.94 | 863.53 |
| Total expenses | 705.91 | 600.45 |
| Net profit for the year | 205.65 | 244.93 |
Cash flow Statement
| Key Metrics | FY 2023 (INR crore) | FY 2022 (INR crore) |
|---|---|---|
| Cash Flow from Operating Activities | 137.11 | 1,441.75 |
| Cash Flow from Investing Activities | 111.33 | 979.9 |
| Cash Flow from Financing Activities | 185.51 | 8.94 |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the year | 452.99 | 886.94 |
Read Also: TCS Case Study: Business Model, Financial Statement, SWOT Analysis
BSE SWOT Analysis
Strengths
⦁ The BSE is Asia’s oldest stock exchange and commands high recognition among investors, intermediaries, and the public in India.
⦁ The company has made strategic decisions regarding the careful selection of open-source technologies and their applicability, which has helped it save money and allow for more investment in other strategic areas of the business. As a result, the company has been able to stay competitive and innovative in the market.
⦁ It has also improved its position as a market leader in using AI and ML for surveillance and monitoring in Big Data initiatives.
Weakness
⦁ The BSE encounters robust competition from other stock exchanges, notably the National Stock Exchange (NSE) in India, the BSE needs to consistently enhance the efficiency of its platform in order to remain competitive.
⦁ There is a prevailing notion that the BSE exhibits a perceptibly bureaucratic organisational framework in comparison to recently emerged exchanges. This may result in slower decision making and impede the company’s capacity to promptly adjust to evolving market conditions.
⦁ The BSE may have a relatively smaller proportion of retail investors in comparison to the NSE, which could significantly impact its reach and overall trading volume.
Opportunities
⦁ Recently, BSE has launched trading in SENSEX and BANKEX derivative contracts. The exchange can launch more contracts for trading, which will increase its revenue potential.
⦁ The BSE expresses confidence in playing a transformative role in developing a vibrant gold spot exchange through the trading of Electronic Gold Receipts (EGR), with the aim of ensuring maximum participation from across the country.
⦁ BSE Ebix (Insurance broking platform) plans to expand its distribution network by partnering with more wealth management advisors and Point of Sales Persons (PoSPs) to sell both life and non-life insurance products.
Threats
⦁ Adverse macro-economic developments and political uncertainty have the potential to diminish the sentiments of the capital markets and exert a negative impact on the exchange business.
⦁ The current competitive landscape for the securities transactions business in India remains increasingly formidable. Companies’ ability to compete and ensure fair regulations will be crucial for sustained growth and profitability.
⦁ Capital markets are a prime target for cybercriminals due to the large sums of money involved. Such attacks are more destructible as compared to other industries, which can have a huge impact on business, affecting brand, customer trust, and investors’ interest.
Read Also: LIC Case Study: Business Model and SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
The BSE’s story is one of the remarkable resilience and adaptation. From its humble beginnings under a banyan tree to its current position as a leading stock exchange, it has consistently played a key role in India’s financial growth. India’s growing economy makes BSE a thrilling platform for wealth creation and an intriguing entity to monitor in the future.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the BSE?
The Bombay Stock Exchange, or BSE, is a stock exchange located in Mumbai, India. It is the oldest exchange in Asia.
What is the BSE’s benchmark index?
The BSE Sensex is a vital stock market index that tracks the performance of the top 30 companies listed on the exchange by market capitalisation.
Is BSE a listed company?
Yes, BSE is a listed company and currently trades at a market price of INR 2,850 (as of 6 May 2024) on the National Stock Exchange (NSE).
Does the BSE offer electronic trading?
Yes, as of May 2024, the BSE operates on a fully electronic trading platform for efficient and secure transactions.
Does the BSE offer trading in equity index derivatives?
Yes, as of May 2024, the BSE offers trading in three derivative contracts, i.e., SENSEX, SENSEX 50, and BANKEX.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.