| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Jul-10-24 | |
| Add new links | Nisha | Feb-18-25 | |
| Add new links | Nisha | Feb-18-25 |

- Blog
- business cycles
Business Cycles of a Company

Businesses operate in a dynamic economic environment, with various economic factors impacting their operations simultaneously. Each company experiences many fluctuations in economic activity over its operational time.
Every equity investor in a company is a partial owner of the company due to which investors should understand the business’s current phase and its characteristics to make better investment decisions. In today’s blog, we will discuss various phases of the business cycle and their impact on the company, along with an example.
What is the Business Cycle?
A business cycle refers to the fluctuations in a country’s economic activities that a company experiences over time. These fluctuations are part of a cycle of expansion and contraction and are influenced by various external economic factors. Significant factors include market demand and supply, government policies, and global economic conditions. Every company’s business cycle has five phases, which are explained below.
Read Also: Different Types of Companies in India
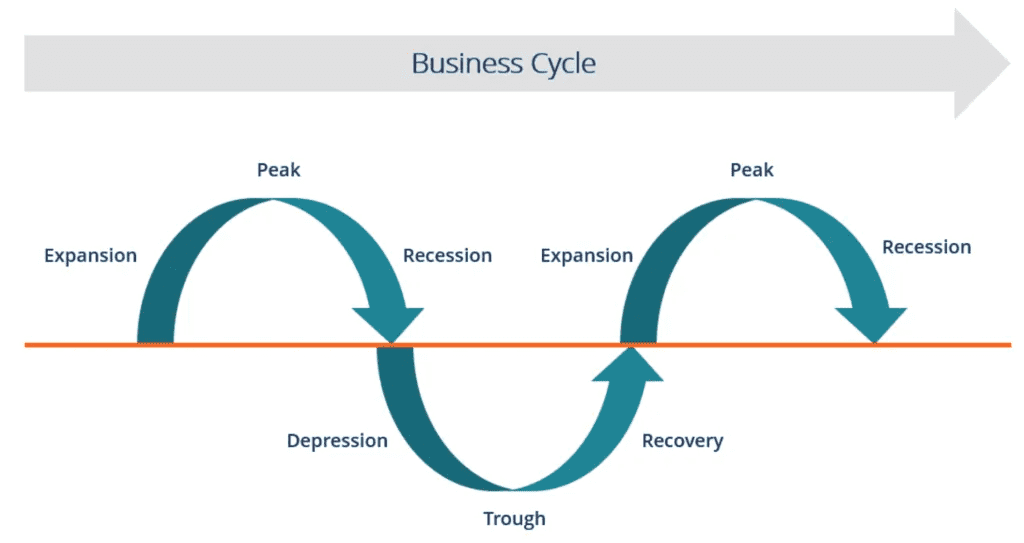
Five Phases of a Company’s Business Cycle
The five phases of a company’s business cycle are influenced by different factors impacting the business environment in which they operate. Understanding each of these phases can help investors decode the reason behind the company’s performance in a specific year. The five phases of the company’s business cycle are:
1. Expansion Phase
The expansion phase is the initial phase where a company grows in terms of revenues and profits. During this phase, a company experiences growing demand for its products or services, leading to increased sales and revenues. It is a phase of upward economic trends, with high consumer confidence and a favorable market environment.
During this phase, companies invest in new projects, increase their workforce, and expand their operations. For example, a tech company might launch new products or expand into new markets as demand for the latest technology grows.
2. Peak Phase
The peak phase represents the height of economic activity in a company’s business cycle. During this stage, a company’s growth reaches its maximum limit, where the production, sales, and revenue growth rates are at their peak. However, this phase is generally short-lived as the market becomes saturated.
At this point, a company must prepare to transition into the contraction phase. A common example of a company in the peak phase is a retailer selling gifts and sweets during the festival season. The demand for gifts and sweets is at its peak during the festive season.
3. Contraction or Recession Phase
Following the peak phase, the economy contracts in the third phase, and two consecutive quarters of contraction are generally considered a recession. It is known as a period where economic activity begins to decline. During this phase, sales decrease, production slows, and the overall economic climate worsens. The decrease in production activities reduces the demand for raw materials and impacts other businesses. This decline can be triggered by market saturation, decreased consumer spending, or broader economic downturns. An extremely severe recession is known as a depression, which generally occurs when the GDP declines more than 10%.
Companies generally reduce their workforce, cut costs, or halt expansion plans during this period. For example, in this phase, a retailer reduces the number of employees and focuses on high-margin products to maintain cash flow when the number of customers declines.
4. Trough Phase
The trough phase represents the lowest point in the business cycle. The economic activities are minimal at this stage, and the growth rate becomes negative. Also, the situations within and around the company are generally negative. However, it is also a crucial time for making critical decisions that affect a company’s future trajectory. Companies often streamline operations to improve efficiency, which includes automating certain processes or consolidating operations to reduce operational costs.
The trough phase is a time for reevaluating and possibly overhauling business strategies. Companies might explore new markets or different customer segments to serve. An example of a company in the trough stage is a manufacturing firm optimizing its production lines for efficiency during low-demand periods to reduce operational costs.
5. Recovery Phase
The recovery phase signifies the beginning of an upward trend in the company’s business cycle. It shows a gradual increase in consumer confidence, spending, and overall economic activity. During this time, companies start reinvesting in areas scaled back during the contraction and trough stages. These include marketing, new product development, and workforce expansion. As the market recovers, companies expand their operations or enter new markets to capitalize on growing demand.
Now, businesses must monitor the market and adapt their strategies as needed. Timely decisions help them capitalize on early recovery-stage opportunities. An example of a company in the recovery stage is an automobile company that begins to increase its production as the market demand grows and the economy recovers.
Illustration of Different Stages of Business Cycle
Decoding the Business Cycle of Reliance JIO Industries
Reliance Industries can be used as an example to understand the different phases of a company’s business cycle over the years. During the expansion phase, the launch of Reliance Jio in 2016 led to rapid growth and significant market capture in the telecom sector. The peak phase was evident around 2018-2019 when Jio became India’s largest telecom operator, and other business segments thrived.
The contraction phase occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic, with reduced demand and operational challenges. In the trough phase, Reliance focused on strategic adjustments and raised capital from major investors like Facebook and Google. Post-pandemic, the company entered a recovery phase, emphasizing digital expansion and retail growth, demonstrating resilience and adaptability.
Conclusion
The business cycle of a company conveys the economic environment in which it is operating. Several factors affect the company’s business cycle, including the demand and supply of its products and services, capital availability, inflation, and consumer spending. Understanding these factors helps investors better forecast the phases in the near future and ultimately predict the company’s future performance, but always consult your financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is it important for equity investors to understand the business cycle?
Equity investors must understand the business cycle as it helps them anticipate changes in the company’s performance, manage risks, and make informed decisions about buying or selling shares.
How does the expansion phase affect a company’s strategy?
A company typically experiences increased demand for its products during expansion. It leads to higher sales and revenue. Higher demand prompts the company to invest in new projects, expand operations, and hire more staff to capitalize on favorable market conditions.
What signals the transition from the peak phase to the contraction phase?
The transition from the peak to the contraction phase is often signalled by market saturation, where the rate of production and sales reaches its maximum and begins to decline. This phase may also start as consumer demand decreases or external economic conditions worsen.
What strategic decisions are critical during the trough stage?
During the trough stage, companies must make strategic decisions regarding operational efficiency, cost management, and potential market repositioning. This stage is also suitable for reevaluating and possibly overhauling business strategies to prepare for the next growth cycle.
How do companies prepare for the recovery stage?
Companies prepare for recovery by gradually reinvesting in key areas such as marketing, new product development, and workforce expansion. It is also important for businesses to stay agile, closely monitoring the market and adapting strategies to capitalize on early signs of recovery.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.