| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Dec-30-24 | |
| Infographic Updated | Ranjeet Kumar | Apr-12-25 |
Demat Account Charges Comparison 2025

In 2025, selecting the right Demat account is crucial for retail and institutional investors as India’s financial markets expand. Demat accounts play an important role in the electronic holding and trading of securities. However, understanding the fees related to these accounts is essential for maximizing your returns.
This blog explains the types of demat account charges and compares demat account charges.
Why Should You Compare Demat Account Charges?
Demat accounts have various visible and hidden fees that can impact investment costs. Investors can boost their returns and minimize costs by comparing account opening fees, maintenance charges, transaction fees, and other related expenses.
Types of Demat Account Charges
Before we start with the comparison, it is essential to know the main types of demat account charges as listed below:
- Account opening charges: It is a one-time charge that is incurred for opening a demat account.
- Annual maintenance charge (AMC): It is a yearly fee for keeping your demat account active.
- Brokerage charges: These are the costs incurred for executing trades on the platform.
- Dematerialization and Rematerialization charges: Fees for converting securities from physical to electronic forms and vice versa.
- Off-market transaction charges: Fee applicable for transferring securities between demat accounts.
- DP Charges: These charges refer to the fees imposed by depository participants on behalf of depositories such as CDSL or NSDL for holding your securities
- Pledging Charges: These are the charges that are applied by the broker when securities are used as loan collateral or fulfill margin requirements.
Comparison of Demat Account Charges Across Popular Brokers
| Broker | Account opening charges | Account maintenance charge | Dematerialization and Rematerialization charges | Brokerage Charges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pocketful | 0 | For non-BSDA accounts 1. For Individuals: First year free, then Rs.70/- + GST charged quarterly. 2. Non-Individual: Rs. 1,000/- + GST charged quarterly. 3. NRI: Rs.500/- + GST For BSDA Accounts 1. Up to Rs. 4 lakhs: Nil 2. More than Rs. 4 lakhs but up to Rs.10 lakhs: Rs. 25/- + GST (Charged Quarterly) 3. More than Rs.10 lakhs: Not a BSDA. Regular AMC may be levied. | 1. Demat: Rs. 150/- per certificate 2. Remat: Rs. 150/- per certificate + CDSL Charges | 1. Equity Intraday: Rs. 20 per executed order or 0.03% of turnover, whichever is lower 2. Equity Delivery: Rs. 20 per executed order or 0.05% of turnover, whichever is lower 3. Futures- Rs. 20 per executed order or 0.03% of turnover, whichever is lower 4. Options-Rs. 20 per executed order |
| Zerodha | 1. Online Account: Free 2. Offline Account: Free 3. NRI Account (offline only – INR 500 | 1. For BSDA: Rs. 0 if holding > INR 4 Lakh 2. Non-BSDA: INR 300/year+18% GST charged quarterly | 1. Demat (Per certificate) : Rs. 150/- per certificate. 2. Remat (Per certificate): Rs. 150/- per certificate+ CDSL Charges Courier charges of Rs. 100 are applicable for each demat/remat request. | 1. Equity Delivery: Rs.0 2. Equity Intraday: 0.03% or INR20/ executed order, whichever is lower 3. Futures: 0.03% or INR 20, whichever is lower 4. Options: Rs. 20 per executed order |
| 5 Paisa | Free | 1. For BSDA a) 0 per month if your holding value is less than INR50,000 b) INR 8 per month if your holding value is INR 50,000 to INR 2,00,000 c) Rs. 25 per month if your holding value is above INR 2,00,000 2. For Non-BSDA: INR 25 per month | 1. Demat – INR 15 per certificate 2. Remat – INR 15 per Certificate ORper 100 Units/shares(whichever is higher) | 1. Equity Cash/ Equity F&O: INR 20 per order |
| Angel One | 0 | 1. For Non-BSDA: INR 60 + GST per quarter 2. For BSDA: a) NIL if Holding Value less than INR 4,00,000.00 b) Rs. 100 + GST per year if holding value greater than Rs. 4 lakh and less than Rs. 10 lakh c) Holding value above Rs. 10 lakh is a non-BSDA account. | 1. Demat: INR 50 per certificate 2. Remat: INR 50 per certificate + Actual CDSL Charges | 1. Equity Delivery: Rs. 0 up to Rs. 500 for first 30 days. Then lower of INR 20 or 0.1% perexecuted order, a minimum INR 2 2. Intraday: Rs. 0 brokerage up to Rs. 500 for first 30 days, then lower of INR 20 or 0.03%. 3. F&O: Rs. 0 brokerage up to INR 500 for the first 30 daysthen, INR 20 per executed order |
| Upstox | 0 | Only for those accounts opened before August 2021 1. AMC of INR 150 + GST = ₹177/- 2.Quarterly maintenance charges of ₹75 + GST = ₹88.50/- (as applicable as per offer/plan) | 1. Demat: INR 200 per share certificate, INR 50 for courier services +18% GST. 2. INR 25 for every certificate | 1 . Equity Delivery: INR 20 per executed order 2. Equity Intraday: INR 20 or 0.05%, whichever is lower 3. Futures: INR 20 or 0.05%, whichever is lower 4. Options: INR 20 per executed order. |
| Groww | 0 | 0 | Demat/Remat – INR 150 per certificate + courier charges. | 1. Equity: INR 20 or 0.05% of order value, whichever is lower. 2. F&O: INR 20 per executed order |
Read Also: Eligibility Criteria to Open a Demat Account
Also, there are two types of demat accounts,
- BSDA (Basic Services Demat Account): This account is meant for investors with smaller investments and has lower or no maintenance charges.
- Non-BSDA or Regular Demat Account: This account suits active traders and investors with higher investment volumes and usually involves higher maintenance charges.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Demat Account
Various factors to consider before choosing a Demat account are:
- Demat Account Charges: Certain brokers impose fees for opening a demat account, while others provide the service at no cost. When opening a demat account, an individual should factor in the amount of the account opening fee and AMCs.
- Brokerage: Compare brokerage rates for intraday trading, delivery trades, and future & options trading. Choose discount brokers for frequent trading as they generally offer lower fees than full-service brokers.
- Trading Platforms and Tools: Make sure the broker offers a dependable and user-friendly platform for trading on mobile applications. Look for advanced features such as real-time charts, technical analysis tools, and quick execution speed.
- Regulatory compliance and Ratings: Check if the broker is registered with regulatory authorities such as SEBI. You can go through the customer reviews and ratings on the internet to assess the reliability of their service.
- Customer support: Seek brokers that provide fast and easy customer service via phone, email and live chat. Also, check their service hours and availability during trading hours.
- Nomination services: Select a broker that lets you choose a nominee to protect your investment. Use brokers with strong security measures like two-factor authentication to safeguard your account.
- Geographic reach and branch network: If you value in-person support, consider choosing brokers that offer an extensive branch network. Assess their capability to offer services in various cities or regions.
- Account closure and Transfer process: Check the process and any fees for closing your account or transferring holdings to a different demat account.
Hidden Charges to Watch out for
You must be aware of the hidden charges associated with a Demat account:
- Call & Trade Charges: These are fees charged for placing orders via phone with your broker instead of using online trading platforms. If you find yourself unable to execute trade online because of technical difficulties, you can choose the call & trade option.
- Stamp Charges: This is a kind of tax imposed by the government on the value of security traded in your account. It is charged during the purchase of stocks and other assets.
- Account with Debit Balance: It is a penalty or interest imposed on a demat account because of insufficient funds for unpaid balances.
- Margin Trading Facility (MTF): It is a facility that allows investors to borrow funds from the broker to trade larger positions than their available cash balance. Additional interest charges are imposed when an individual avails margin facility to buy shares.
- DIS Slip Request Charges: DIS stands for delivery instruction slips. These are the charges levied for obtaining DIS booklets to transfer shares offline between demat accounts. It is applicable for manual share transfers instead of online ones and is often needed by investors with accounts at different DP.
- DDPI Charges: DDPI stands for Demat Debit and Pledge Instruction. These charges are levied when issuing DDPI, which allows brokers to debit or pledge securities from an individual’s demat account.
How Can I Reduce My Demat Charges?
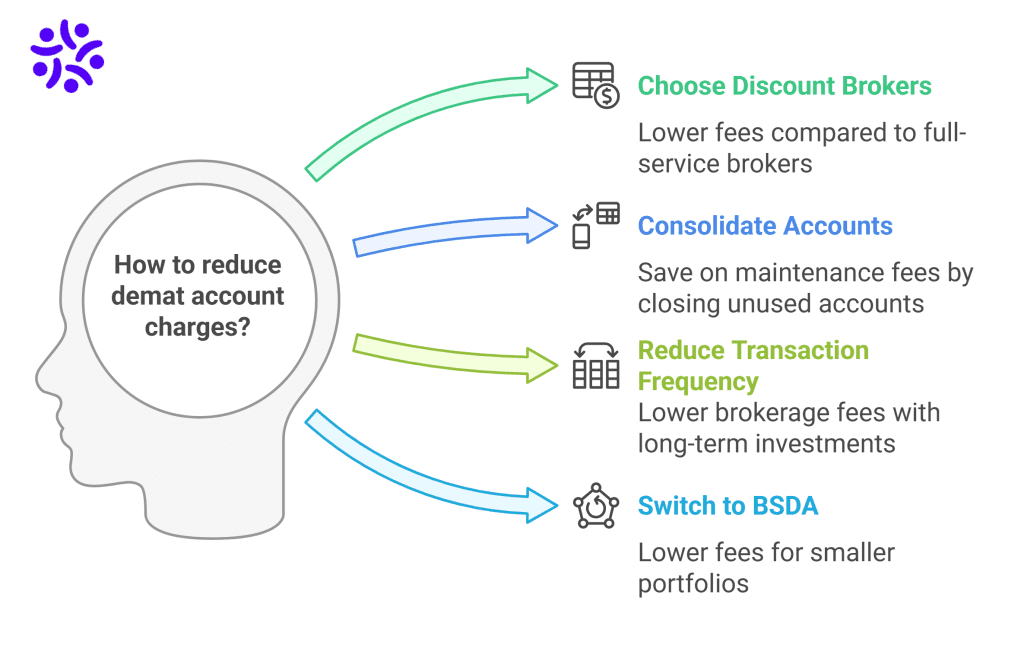
Lowering your demat account fees can improve your investment returns. Some of the points by which you can reduce your demat charges are listed below:
- Choose discount brokers because they usually have lower account opening fees, AMC, and transaction costs than full-service brokers.
- Avoid having multiple demat accounts unless necessary since each one has its own maintenance fees. Transfer holdings from unused accounts to your active account and close dormant accounts to save on AMC.
- Reduce the frequency of transactions because every trade comes with transaction fees. Choose long-term investments instead of high-frequency trading (HFT) to lower brokerage fees and other costs.
- If your portfolio is worth up to ₹4,00,000 in India, you can think about switching to a BSDA or basic service demat account.
- Evaluate your broker’s performance and fees regularly. If you are paying high fees or their services are unsatisfactory, you can consider transitioning to a more cost-effective broker that offers better options.
Conclusion
Selecting the ideal broker for a demat account involves striking a perfect balance between cost-effectiveness and the variety of features available. Choose the platform that matches your financial goals and trading style, has lower fees, advanced features and offers personalized support. By assessing the fees, services and benefits, you can make a smart decision to enhance your investment returns in 2025. It is advised to consult a financial advisor before investing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a demat account, and why do I need it?
A demat account is used to hold financial assets such as stocks, bonds, and ETFs in electronic form. It removes the need for physical share certificates and ensures faster, secure trading in the stock market.
Can I open a demat account without linking it to a trading account?
You can open a standalone demat account to store securities. However, if you want to trade in the stock market, you will need a trading account as well.
Are there any hidden charges I should watch out for?
Some of the common hidden charges include call & trade fees when using customer support and higher AMC after initial promotional periods.
Can we maintain 2 demat accounts?
You can open multiple demat accounts with different DPs.
What is the difference between CDSL and NSDL?
CDSL and NSDL are two depositories in India where your securities are stored, and your demand account is opened at one of these depositories. There is no difference between CDSL and NSDL as both provide the same services and are regulated by the SEBI.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.