| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Nov-07-23 | |
| Add new links | Nisha | Feb-21-25 | |
| Add new links | Nisha | Feb-21-25 |

- Blog
- different types of charges in online trading
Different Types of Charges in Online Trading
The process of buying and selling financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, and derivatives, through your demat account in electronic form is known as online trading. Individuals and institutional investors trade and invest in various financial markets from the comfort of their homes to earn and generate good returns over time. The online trading platforms provide their customers with hassle-free trading facilities, thereby increasing the popularity of online trading. These platforms offer user-friendliness, convenience, and real-time access to financial markets. Later in this blog, we will be discussing these platforms in detail.
Before we proceed further, here is an overview of some characteristics of trading online
What is Online Trading
The platforms involved in online trading allow traders to execute their buy/sell orders whenever they want to help them access & analyze market data, and manage their holdings of stocks.
Traders can place various types of orders while trading online, such as market orders, limit orders, and stop-loss orders, which help traders decide their entry and exit points.
Investors can have access to different financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, options, futures, foreign exchange, etc. This allows the investor to diversify their portfolio and minimize risk since Warren Buffet once said “Don’t keep all your eggs in one basket”.
Online trading is often cost-effective and has lower transaction fees and charges when compared to traditional brokerage services.
Proper rules and encryption followed by broker houses, provide a guarantee to the client about the safety of personal and financial information of the investor when he/she trades online.
Online trading platforms provide real-time market data, including current market prices, candlesticks charts, news, and analysis. Traders can make informed and sound decisions since these platforms provide them with accurate information about the market.
A Brief Introduction to Brokerage Firms

Broker houses also known as brokerage houses or brokerage firms, are financial companies that enable easy buying and selling of stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies for traders and investors. These institutions play a vital role in financial markets by connecting buyers and sellers and helping them in trade execution.
Some of the important functions of broker houses or brokerage firms are listed below
- Brokerage firms execute buy and sell orders from their clients in various financial markets, including stock exchanges, commodity markets, and foreign exchange markets.
- Many broker houses provide research reports, market insights, and analysis services to their clients, which eventually helps them build investment portfolios that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Many broker houses offer their clients margin trading facilities, allowing clients to trade with extra funds, which can increase profits and losses.
- These firms also provide educational resources and training either through social media or their websites to help clients have a clear understanding of the stock market.
Types of Brokerage Houses

Broker houses can differ in terms of the services that they are offering, the markets they specialize in, and their fee structures. There are two main types of brokerages:
1. Full-Service Broker Houses:
These houses offer a variety of services, including investment advice, research, mutual funds etc. They charge higher fees and help their clients in managing their portfolios, retirement planning, and wealth management. They help their clients in choosing the investment option as per his/her risk appetite and time horizon.
- HDFC Securities: It is a subsidiary company of HDFC Bank, and offers a range of trading and investment services, including equities, derivatives, mutual funds, and more.
- ICICI Direct: ICICI Direct is the retail trading and investment company of ICICI Bank. It provides online trading services for equities, derivatives, commodities, mutual funds, etc.
2. Discount Broker Houses
These broker houses offer fewer services as compared to full-time brokerage houses and their main focus is on order execution. They are generally cost-efficient and are popular among self-reliant investors and traders. A few examples of the same are as follows:
- Zerodha – It is one of the leading and well-recognized discount brokerage firms in India and is famous among traders for the services it provides. It offers trading not only in equities but also in commodities, currencies, and derivatives.
- Pocketful – It is also a discount brokerage firm that provides online trading services for equities, derivatives, and commodities.
Full-service brokerages are befitting for clients who wish to have personalized assistance and are willing to pay higher fees, while discount brokerages are meant for independent investors looking for cost-efficient trading options.
Having known the benefits of online trading and types of broker houses let us go through the detailed explanation of various charges that an investor needs to pay to the broker while trading online.
Read Also: Demat Account Charges Comparison 2025
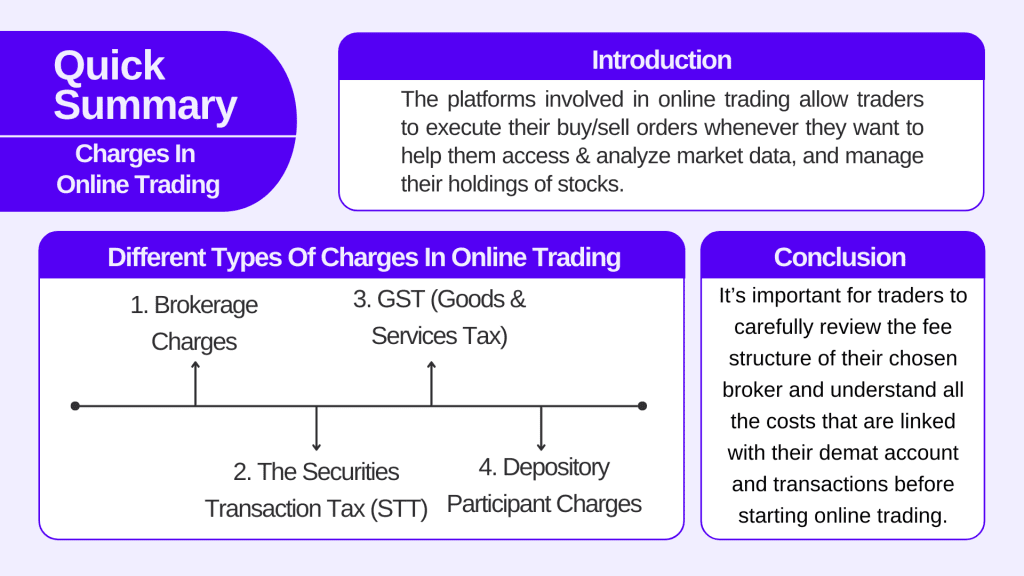
Different Types of Charges in Online Trading
1. Brokerage charges
These charges also known as brokerage fees or commissions, are the fees that investors pay to brokerage firms for executing buy and sell orders for various financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds, options, futures, and more. These charges can differ from company to company depending upon the type of brokerage and the specific services offered.
These charges apply to buying and selling stocks in the equity markets as well as futures and options.
2. The Securities Transaction Tax (STT)
STT is a tax which is levied on the value of securities transactions in India. It was introduced in 2004 and is applicable to various securities, including equities, derivatives, and equity-oriented mutual funds. The STT helps the Government of India to collect revenue and to regulate financial markets. It is borne by the investor or trader and is collected by the stock exchange on behalf of the government.
The STT rates may change based on the type of transaction
If you carry stocks on delivery i.e., for next day STT applicable is 0.1% of the transaction value.
For intraday STT applicable on securities is 0.025% of total value
The STT is collected by the stock exchanges from the brokers, who, in turn, collect it from their clients.
3. GST (Goods & Services tax)
When you pay brokerage charges or service charges to your brokerage firm a GST of 18% is already included.
4. Depository Participant Charges
A Depository Participant (DP) is an entity that acts as an intermediary between the investors and the central depository or CDSL. DPs facilitate the holding and transfer of securities from one brokerage firm to another in electronic form.
Below mentioned are some common DP charges in India:
- Account Opening Charges: DPs may charge an account opening fee when you open a Demat account with them. The account opening fee is a one-time payment made by the client and may differ from DP to DP.
- Annual Maintenance Charges (AMC): DPs generally levy an annual maintenance charge for maintaining your Demat account. This fee is paid annually that is once a year.
- Account Closure Charges: When you decide to close your Demat account with a DP, you need to pay a certain amount as charges and also you have to clear your debit balance if any.
The charges of Mutual Funds are described below
- Expenses Ratio/Management Fees – When you invest in mutual funds, the Asset Management Company will charge a fee to manage your portfolio. This is called the expense ratio or management fees. The expense ratio ranges from 0 to 2.5%. These charges are deducted from your investment.
- Entry Load – Earlier in 2009, investing in mutual funds attracted an entry load, which meant when you invest in mutual funds, you will end up paying some amount to the asset management company that too at the time of investment. However, this was abolished by SEBI in the year 2009.
- Exit Load – This charge is payable by the customer on the redemption made by them before the prescribed investment period. This exit load may vary from 0.5% to 3%, depending on the fund. The exit load is deducted before the proceeds are paid out.
Read Also: What is a Stock Broker? Meaning, Features, Types, and Commissions Explained
Conclusion
It’s important for traders to carefully review the fee structure of their chosen broker and understand all the costs that are linked with their demat account and transactions before starting online trading. The fee structure and charges can significantly impact the profitability of the trader, so it’s essential to factor these costs into trading strategies and decisions. Additionally, traders should consider other aspects, such as the quality of services and trading conditions, when choosing a brokerage firm
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Do I need to pay charges for trading?
Yes, you need to pay charges for trading.
What are brokerage charges?
Brokerage charges, also known as brokerage fees or commissions, are the fees that investors pay to brokerage firms for executing buy and sell orders of financial assets.
What is Discount Broker?
These broker houses offer fewer services, and their main focus is on order execution. They are generally cost-efficient and are popular among self-reliant investors.
Is STT paid on mutual funds?
Yes, STT is payable on mutual funds also.
Explain DP charges.
Charges levied by DP for holding the securities in your demat account.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.