| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Dec-21-23 | |
| Update Content | Nisha | Mar-18-25 | |
| Infographic Update | Ranjeet Kumar | Apr-03-25 |

- Blog
- dmart case study business model and marketing strategy
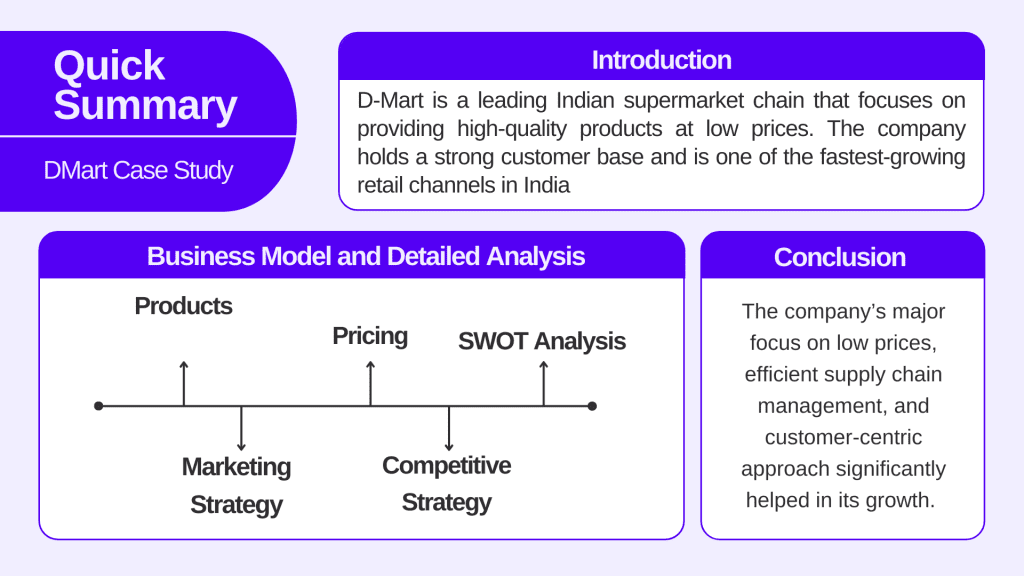
D Mart Case Study: Business Model and Marketing Strategy


D-Mart is a leading Indian supermarket chain that focuses on providing high-quality products at low prices. The company holds a strong customer base and is one of the fastest-growing retail channels in India. D-Mart has been able to achieve all this through well-organized supply chain management.
Let’s explore the Business Model, Marketing Strategy, and SWOT analysis of D-Mart.
D-Mart Company Background
D-Mart was founded in 2002 by Radhakishan Damani, a well-known businessman and a value investor. The company opened its first store in Bombay, and since then it has opened over 250 stores across 11 states and 1 union territory. It took DMart almost eight years to start its ten stores.
D-Mart is listed as Avenue Supermarts Limited on both the stock exchanges, i.e., NSE & BSE, with a current market price of around INR 4,000 and a P/E (Price-earnings) ratio of around 110.
Ever since the IPO in the year 2017, the company’s share price has risen almost 550% from its listing price. Further, it has generated an annualized ROCE of almost 20%, which means 20% returns on the capital employed by Dmart.
In the year 2022-23, the company has opened 40 new stores. The company faces tough competition from giants like Reliance Retail, Big Basket, and Spencers.
D-Mart Subsidiary Companies
- AEL (Avenue E-commerce Limited): A subsidiary company of D-Mart, founded in November 2014, is a multi-channel grocery retail. AEL allows its customers to order a wide range of groceries online through its mobile app.
- Nahar Seth & Jogani Developers (NSJDPL): A subsidiary company of D-Mart, was founded in the year 2014 with the aim of development and construction of land.
- Reflect Healthcare & Retail Private Limited (RHRPL): A wholly owned subsidiary company founded in the year 2018 and operates in the healthcare business.
Read Also: Flipkart Case Study- Business Model and Marketing Strategy
Market Information of D-Mart (Avenue Supermarts Ltd.)
| Current Share Price | ₹3,822 |
| Market Capitalization (in ₹ Crores) | 2,48,694 |
| 52-Week High | ₹5,485 |
| 52-Week Low | ₹3,337 |
| P/E Ratio | 91.5 |
| Face Value | ₹10 |
Business Model of D-Mart
The D-Mart follows a cluster-based expansion approach, i.e., its major focus is on the area where it already exists instead of focusing on new regions with the mission of being the lowest priced retailer in the area of operation.
Also, D-Mart operates on a B2C (Business to Consumer) approach, i.e., goods are sold directly from the manufacturer to the ultimate consumer.
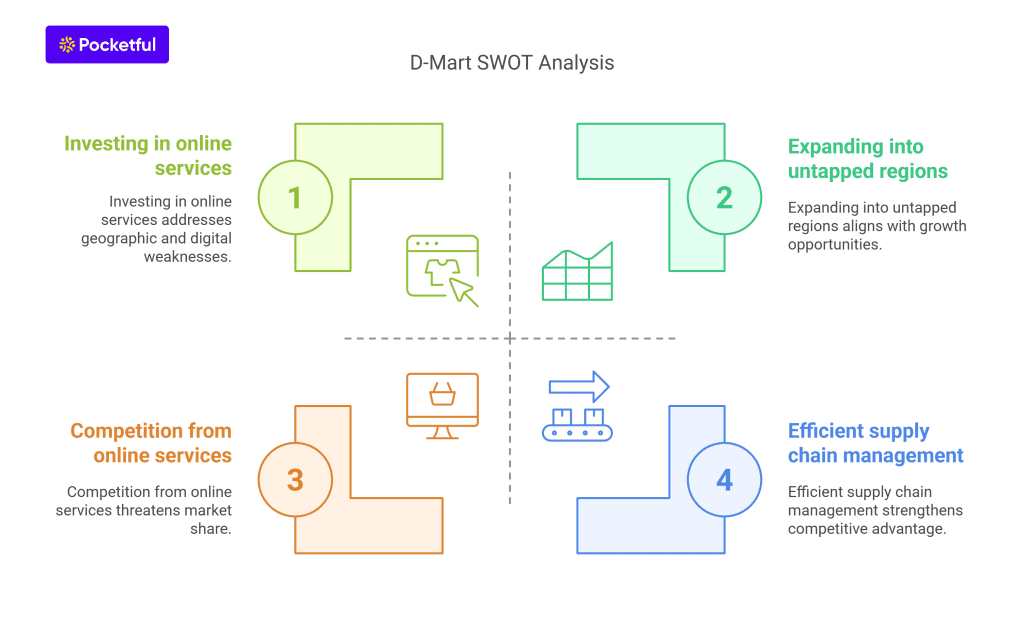
As of March 2024, the company’s store count stood at 365. Major locations of operation include Maharashtra, Gujarat, Telangana, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, NCR, Chhattisgarh, and Rajasthan.
Products of D-Mart
D-Mart provides its customers with multiple daily-use things. It majorly deals in three categories:
- Foods: It includes groceries, processed food, frozen food, staples, beverages, fruits, and vegetables. This segment contributes almost 55% of the revenue of the company.
- Non-Foods: It includes home care products, personal care products, and other OTC products. This segment contributes around 20% to the revenue of the company.
- General Merchandise & Apparel: It includes toys, games, garments, clothes, footwear, utensils, and home appliances. This segment contributes around 23% to the revenue of the company.
As per annual reports of 2023-24, the company has 365 stores, 62 distribution centres, 10 packing centres and had a total of 13,971 employees.
Pricing of D-Mart
Giving low prices to customers is the USP of D-Mart. It focuses on EDLC / LP pricing strategy (Everyday Low Cost & Price). In the D-Mart stores, the prices of the products are significantly lower than the MRP.
This pricing strategy helps them generate more volume in sales since people who visit stores eventually end up buying multiple other products as well.
D-Mart Marketing Strategy

D-Mart stores are generally large and spacious, providing the customer with a good shopping experience. It majorly focuses on Word-of-mouth marketing and In-store promotions rather than expensive marketing campaigns. The iconic green label of the company is the billboard itself.
This strategy has helped the company in better market positioning as compared to other retail businesses.
D-Mart Competitive Strategy
How come D-mart overcomes tough competition from giants like Reliance & Amazon?
What made D-mart different from these giants is that the company focused on selling non-fancy products. They try to understand consumer preferences and form a strong relationship with the suppliers.
The company also follows a store-ownership model and is not located in any fancy and highly-priced market. The company generally owns stores in sub-urban regions. This helped them save a lot of money on rental expenses. We are sure that you have never found a store in a mall or posh locality.
To summarise, the company’s competitive strategies are deep discounting, no fancy locations, and ownership. This helped the company to dominate the Indian retail market.
SWOT Analysis of D-Mart
Strengths
- D-Mart’s EDLP strategy helps the company to attract middle-class consumers.
- Efficient supply chain management and smooth operational processes have given the company an immense boost in the retail sector.
- Offering a wide range of products in food and non-food segments at a lower price than MRPs.
- Consistent growth in the revenue and profits of the company is the key strength of the company.
Weakness
- Lack of global presence and less geographic reach with less focus on opening stores in new regions.
- As compared to the competitors, the online presence and promotion of the company is not at par.
- Low pricing strategy of the products can affect the vendors and lead to supply chain disruptions.
- D-Mart stores follow a no-frills approach with simple and basic layouts. This may be unattractive for several customers who love fancy things.
- D-mart charges a slotting fee from manufacturers who want to display their products in stores. This expense might be a deal breaker for the manufacturers who wish to collaborate with D-Mart.
Opportunities
- Focus on penetrating the untapped regions of North & East India.
- Investing in online delivery services for a better presence on the internet can help the company further expand its business.
- Implementing automation technologies in warehouses and distribution centres can streamline operations and reduce costs.
Threats
- An increase in online doorstep grocery services like Blinkit, Jio Mart, etc. can affect the business significantly.
- D-mart operates in the retail industry, which has a low entry barrier. Further, it faces tough competition from local stores and supermarkets.
- Changes in regulations related to the retail sector and anti-competition policies could impact D-Mart’s operations and business model.
Key Performance Indicators (KPI)
| Particulars | March 2024 | March 2023 | March 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Margin (%) | 6.92 | 7.30 | 6.83 |
| Net Profit Margin (%) | 4.99 | 5.55 | 4.81 |
| ROCE (%) | 18.33 | 18.79 | 14.85 |
| Current Ratio | 3.13 | 3.71 | 2.83 |
| Debt to Equity Ratio | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| EV/EBITDA | 69.20 | 58.20 | 98.92 |
Read Also: Nike Case Study: Business Model & Marketing Strategy
Conclusion
D-Mart’s ability to navigate the competitive landscape in India and maintain cost-efficiency deserves a hand of applause. The company’s major focus on low prices, efficient supply chain management, and customer-centric approach significantly helped in its growth. The success story of D-Mart serves as a valuable source of learning for new entrants in the retail sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who founded D-Mart?
Radhakishan Damani founded D-Mart in 2002.
Is D-Mart a listed company?
Yes, D-Mart is a listed company on NSE and BSE.
In which year D-Mart was listed on stock exchanges?
D-Mart was listed on the stock exchanges in the year 2017.
In how many cities D-Mart currently function?
D-Mart currently functions in 20+ Indian cities.
Who is the competitor of D-Mart?
D-Mart faces tough competition from Reliance Retail, Spencers, Big Basket, etc.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.