| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Mar-05-24 | |
| Content Update | Default Author | Mar-29-25 | |
| Content Update | Nisha | Mar-29-25 | |
| Infographic Update | Ranjeet Kumar | Apr-03-25 |

- Blog
- hindustan unilever limited hul case study key acquisitions business model financials and swot analysis
Hindustan Unilever Case Study: Business Model, Financials, and SWOT Analysis

Hindustan Unilever is a household name; almost every product in your bathroom was made by HUL. Today, we’ll explore its business model to understand its operations.
About Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL)
Hindustan Unilever was founded in the latter part of the 1980s. The Lever brothers, established by William Hesketh Lever, first entered the Indian market in 1888 with a product known as sunlight soap. However, the soap was marked with the phrase “Made in England by Lever Brothers”.
Hindustan Vanaspati Manufacturing Company, Unilever’s first Indian affiliate, was founded in 1931. Lever Brothers India Limited followed in 1933, and United Traders Limited followed in 1935. In 1956, these companies amalgamated to establish Hindustan Unilever Limited.
The company’s headquarters is located in Mumbai. Rohit Jawa took over as CEO of Hindustan Unilever Limited in June 2023, replacing Sanjeev Mehta.
After Hindustan Unilever Limited was founded, its primary focus was on acquiring Indian brands that were already well-established.
Key Acquisitions
1984 – Brooke Bond, a tea brand.
1972 – Lipton, a national tea product manufacturer.
2015-16 – Indulekha, a premium hair oil brand.
2019-20 – GSK, a healthcare product manufacturer.
2019-20 – Vwash, a female intimate hygiene product manufacturer
Awards and Recognition
2023 – Winner of the KPMG ESG Excellence award across India’s consumer market sector.
2022- Outstanding Company of the Year by CNBC –TV18
2021 – Best Governed Company Award
2021- Sustainable Factory of the Year award.
2020 – Top performer in the FMCG Category
Read Also: ITC vs HUL: Comparison of India’s FMCG Giants
Products OF HUL
Whether a food and beverage product or a healthcare item, Hindustan Unilever is used by nine out of ten Indian households!
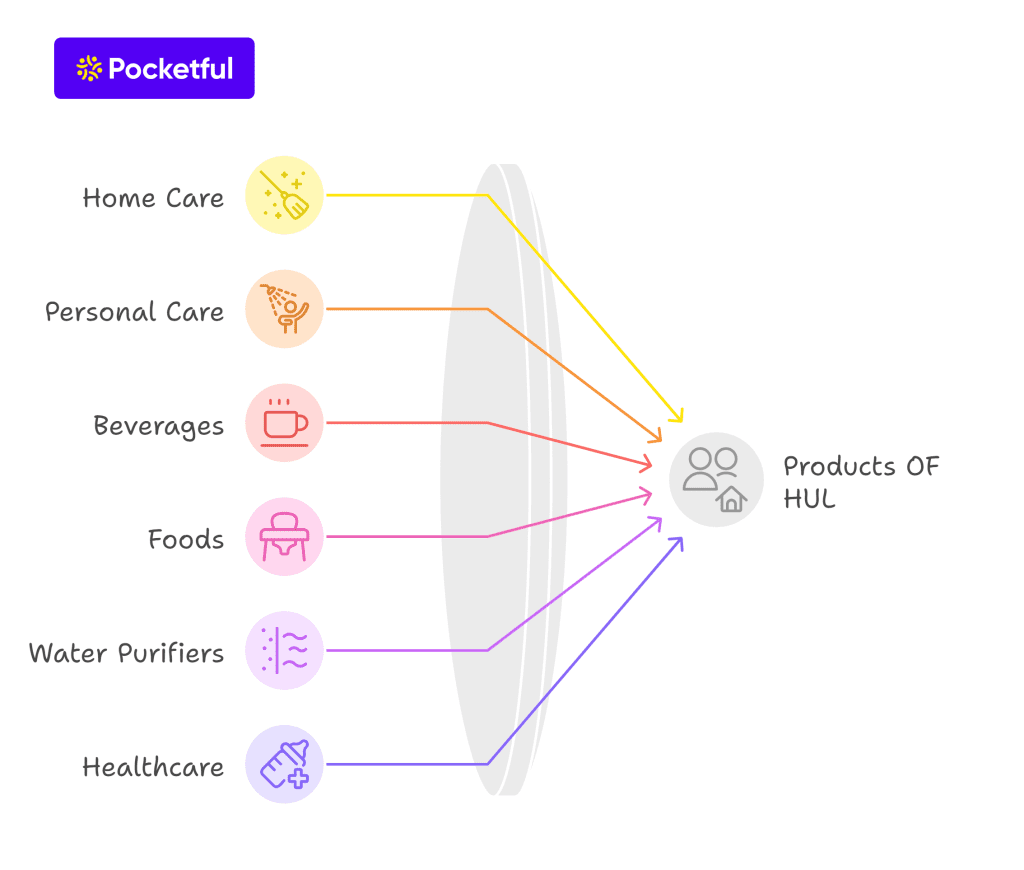
The products of Hindustan Unilever are as follows
- Home care products – Laundry detergents, fabric conditioners, dishwashing liquids, and toilet cleaners. (Surf Excel, Rin, Wheel)
- Personal care products – Soaps, shampoos, skin care products, hair care products, deodorants, oral care products. (Lux, Sunsilk, fair & lovely, Tresemme, axe and closeup, etc.
- Beverages – Tea. (Lipton, brooke bond)
- Foods – Packaged foods.
- Water Purifier – Pureit water purifier.
- Healthcare products – Health drinks. (Boost, Horlicks)
- Baby care products – Baby soaps, shampoos, and body lotions. (Dove, Johnson’s Baby)
- Cosmetic – Cosmetic and beauty products. (Lakme)
Market Information of HUL
| Current Market Price | ₹2,259 |
| Market Capitalization (in ₹ Crores) | 5,30,737 |
| 52 Week High | ₹3,035 |
| 52 Week Low | ₹2,136 |
| Dividend Yield | 1.86% |
| Book Value | ₹216 |
SWOT Analysis of HUL
Hindustan Unilever SWOT Analysis highlights the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, offering valuable insights into its market position and growth potential.
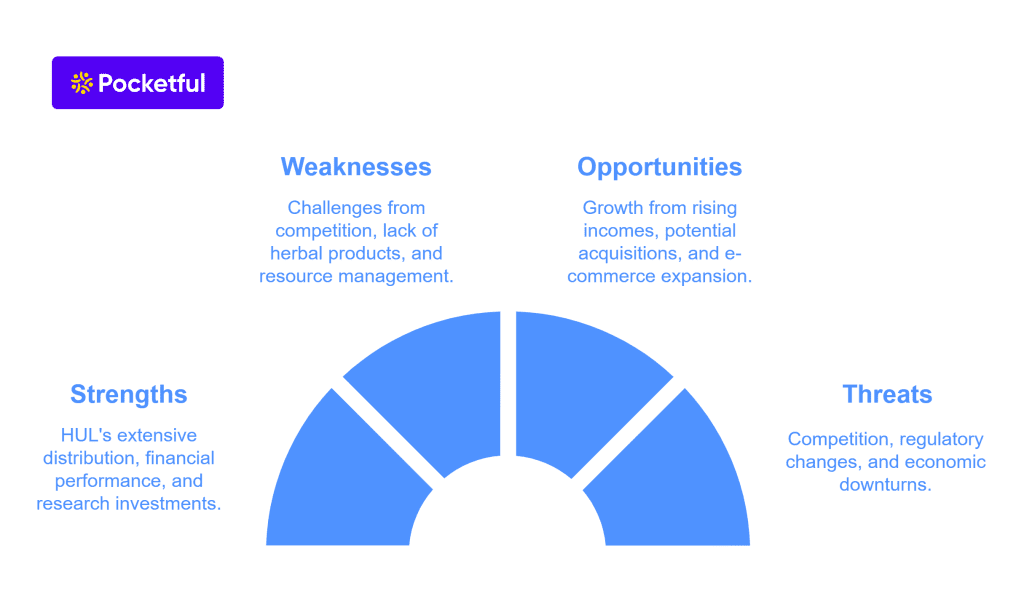
Strengths
- The company’s primary strength is its widespread presence in India, with more than 8 million locations where customers can purchase its product. Its supply chain is excellent, well-managed, and efficient.
- HUL has a long history, which they can preserve because of the money they currently spend on product development and research.
- The company’s financial outcomes demonstrate the impact of its excellent performance.
Weaknesses
- A company’s market share might be reduced by any business that focuses on a certain product.
- Since more and more consumers are turning to herbal items, the corporation may suffer from the lack of any Ayurvedic or natural products in its product line.
- Due to its extensive product portfolio, HUL may encounter difficulties in effectively managing and allocating resources to it.
Opportunities
- The country’s population is likely to have more disposable income in the next few years, which will cause the FMCG sector to grow significantly.
- The business can quickly buy out companies that manufacture goods outside of its current product line, which will aid in product diversification.
- They can expand their customer base and increase revenue by utilizing e-commerce platforms.
Threats
- The business operates in a highly competitive market, and with the advent of globalization, numerous international brands have established themselves in the country.
- Their margins may be impacted by regulatory changes made by the Indian government on food packaging ingredients, labeling, etc.
- A downturn in the nation’s economy may affect consumer buying habits, affecting a company’s profitability.
Read Also: Polycab Case Study: Business Model, Financials, Competitors, and Growth Outlook
Business Model and Marketing Strategy of HUL
The company’s wide range of products enables it to hold the top spot in the market for industrial consumer goods. They have well-known brands in several areas, and their revenue is greatly influenced by consumer recognition of their brands.
Its primary focus is innovation; a sizable amount of its revenue is allocated to creating new items and enhancing its existing line of products.
HUL has an extensive distribution network that reaches both rural and urban locations. Additionally, they invest heavily in all forms of promotion, including print, digital, and sponsorship.
They typically focus on comprehending customer demands and needs because this enables them to develop product lines that cater to consumer preferences
Branding Strategy of HUL
What’s in the name? Though everyone has heard this saying at some point in their lives, it is essential to remember that reputation and brand are everything. The company employs various graphics and logos for its many products, but its distinctive logo is printed on each one, making it easy for the general public to recognize them.
Financials of HUL
Income Statement
| Particulars | March 2024 | March 2023 | March 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Income | 62,707 | 61,092 | 52,704 |
| Total Expenses | 48,443 | 47,632 | 40,724 |
| EBIT | 14,264 | 13,460 | 11,980 |
| Net Profit | 10,286 | 10,145 | 8,887 |
Balance Sheet
| Particulars | March 2024 | March 2023 | March 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Current Assets | 57,175 | 56,089 | 54,995 |
| Current Assets | 21,324 | 16,998 | 15,522 |
| Non-Current Liabilities | 14,200 | 10,537 | 10,150 |
| Current Liabilities | 12,876 | 12,028 | 11,280 |
| Total Shareholder Funds | 51,218 | 50,304 | 49,061 |
Cash Flow Statement
| Particulars | March 2024 | March 2023 | March 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash Flow From Operations (CFO) | 15,469 | 9,991 | 9,048 |
| Cash Flow From Investing (CFI) | -5,234 | -1,494 | -1,728 |
| Cash Flow From Financing (CFF) | -10,034 | -8,953 | -8,015 |
Key Performance Indicators
| Particulars | March 2024 | March 2023 | March 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Margin (%) | 23.03 | 22.32 | 22.92 |
| Net Profit Margin (%) | 16.61 | 16.74 | 16.95 |
| ROE (%) | 20.06 | 20.11 | 18.09 |
| ROCE (%) | 21.72 | 22.14 | 20.29 |
| Current Ratio | 1.66 | 1.41 | 1.38 |
| Debt to Equity Ratio | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Shareholding Pattern
As of December 2024, the company’s promoters own 61.9% of the company’s shares, while Domestic Institutional Investors hold about 14.73%, Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) account for roughly 11.43%, and the public owns 10.34% of the company’s shares.
Read Also: Netflix Case Study: Marketing Strategy, Product Portfolio and Pricing Strategy
Conclusion
The organization has achieved global recognition through its strategic planning and marketing approach. The economy’s overall performance determines HUL’s success, as does the population’s disposable income, which increases company profits.
We have tried to clarify every statistic and data about HUL in this case study, covering everything from their financials, history, and shareholding patterns.
However, always consider your risk tolerance and time horizon before making any investing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Where is the headquarters of Hindustan Unilever located?
The headquarters of Hindustan Unilever is located in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
What was Hindustan Unilever’s former name?
Hindustan Vanaspati Manufacturing Company was the former name of Hindustan Unilever Ltd.
How many factories of HUL are there in India?
HUL currently has 29 factories nationwide.
How many businesses are part of Hindustan Unilever?
There are more than 50 brands connected with Hindustan Unilever.
What is HUL’s market capitalization ranking in the FMCG sector?
Hindustan Unilever ranked at the top among FMCG companies, having a market capitalization of around 5.3 Lakh Crore INR as of 29 March 2025.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.