| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Nov-22-23 | |
| Add new links | Nisha | Feb-25-25 |
Read Next
- Why Are Steel Share Prices Increasing in India?
- Top Nifty Metal ETFs in India 2026
- Best Gold Investment Schemes in India 2026
- How to Build a Portfolio With Exchange-traded Funds (ETFs)
- How to Invest in US Stocks from India
- Platinum Price Forecast in India (2026–2030)
- Why Is the Gold Price Going Down?
- Top 10 BESS Stocks in India (2026)
- Why is the Silver Price Going Down?
- Best Construction Stocks in India
- Why Gold Prices Hit ₹1,80,000 – Key Reasons
- List of Best Sensex ETFs in India
- Best Commodities to Trade in India
- Best Cyclical Stocks in India 2026
- How to Check the Purity of 20-Carat Gold: Easy Methods & Tips
- Why Are Silver Prices Rising in India?
- Difference Between Hallmark Gold, KDM Gold and BIS 916
- Why Are Gold Prices Rising in India?
- 1 Tola Gold in India: How Many Grams, Price & Investment Insights
- 22K vs 24K Gold: Which Is Better for Jewellery & Investment?
- Blog
- how interest rate changes affect the stock market
How Interest Rate Changes Affect the Stock Market
What is Interest Rate?
Interest rate is defined as the price that you pay when you borrow money from someone or it can also be known as income that you earn on your investments like bonds, , and government securities. We will talk about interest rates in the context of lending and borrowing money. Interest rates in India are managed and regulated by RBI and play an important role in the economic growth of a country.
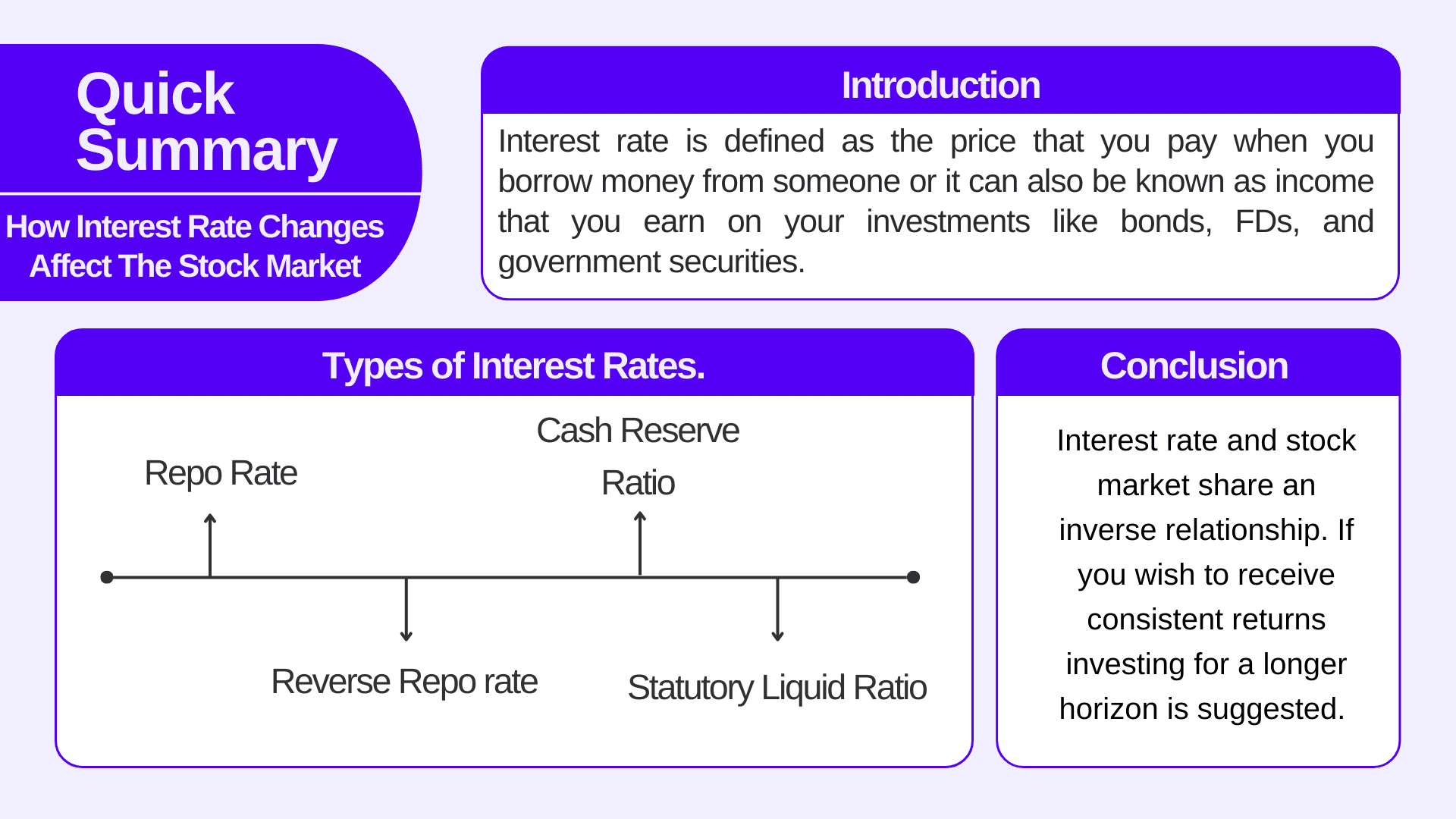
RBI manages various types of interest rates. Let’s have a glimpse at these rates.
- Repo Rate
The rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks. Any kind of change in repo rate can affect the cost of borrowing for banks as well as retail consumers. The repo rate is considered a key tool to control inflation and stimulate economic growth. - Reverse Repo rate
The rate at which RBI borrows money from commercial banks. This rate is comparatively lower than the repo rate. - Cash Reserve Ratio
CRR, or cash reserve ratio, is the amount that commercial banks need to maintain with RBI in the form of cash. Banks do not receive any kind of interest on this from RBI. - Statutory Liquid Ratio
SLR is the minimum amount in percentage that a bank needs to keep either liquid or as investments in government securities.
The RBI uses these interest rates and tools to manage monetary policy, control inflation, and maintain financial stability. Our major focus today will be on the repo rate and how even a slight change can have wide-ranging effects on the broader economy.
Why interest rates are changed?
RBI changes these repo rates as a part of its monetary policy so that it can achieve its financial objectives. Now, what is monetary policy? Policy framed by the RBI to control and manage the supply of money in the economy. Monetary policy can either be contractionary or expansionary. When the money supply is increased and interest rates are reduced. This is known as the expansionary monetary policy. The vice-versa is known as the contractionary monetary policy. Coming back to our topic RBI changes the repo rate because of the following reasons,
- To control inflation in the economy.
- To focus on the economic growth of the economy.
- Situations prevailing in the global economy
The decisions related to the repo rate are made during the RBI’s monetary policy meetings, which occur at regular intervals. Before moving further, we will give you some basic idea about the concept of inflation and deflation. Inflation is the general increase in the price level of goods and services in an economy. Consumers tend to pay more than the actual value of the good. The purchasing power of consumers decreases. In such a case under the monetary policy, the government of India increases the interest rate to fight inflation. This will decrease the flow of money in the economy.
Deflation is the opposite concept of inflation. A general decrease in the price level of goods and services is called deflation. The purchasing power of the consumer is increased. RBI, in this situation, will lower the interest rate in order to increase the flow of money in the economy. We all know that the stock market of any economy is a true indicator that signals the pace of economic growth. So, we need to analyze the fact of how a change in repo rate can impact the markets.
Read Also: How to Start Stock Market Trading With Low or Limited Capital
Impact of rate change on the Indian stock market.
The impact depends on the direction and magnitude of the interest rate changes, as well as the broader economic context.
Interest rates can be changed in two ways
- Interest rate hikes
- Interest rate cuts
When it comes to interest rate hikes, the cost of borrowing money increases which will make it difficult for the companies to avail loans and this will eventually reduce the profitability of the businesses. This will lead to lower earnings of the companies and decreased prices of the stock.
Any sort of increase in the rate of interest can make other investment options more attractive. From the consumer’s point of view, there can be a significant change in his spending habits since there we be lesser disposable income in his hand thereby affecting his savings and investments. Interest Rate cuts, on the opposite side, lead to a decline in the cost of borrowing making it easier for the investor to grow which will lead to higher earnings and higher stock growth.
The immediate impact of interest rate changes on the stock market may vary. Short-term interest rate changes might lead to short-term stock market volatility, while long-term rate trends can have a more lasting effect on the stock market.
Impact of change in rate by the US Federal Reserve on the Indian stock market

Federal Reserve, since we all know is the central bank of the United States, can either increase or decrease the interest rate depending on the situation and needs of the economy. A change in the rate of the U.S. Federal Reserve affects the economy globally. The relationship between the actions of the Fed and the Indian stock market is influenced by several factors. Some of these factors are listed below.
- If the Fed increases the rate of interest, foreign investors will find the U.S. markets more lucrative to invest in. They will withdraw their funds from the Indian stock market and deploy it in the U.S. so that they can enjoy higher returns.
- A slight change in the rate of interest by the Fed can have a significant impact on the exchange rates of currency. If the interest rate increases the U.S. dollar will strengthen and the Indian rupee will weaken.
- If U.S. rates rise substantially, it may lead to higher interest costs for Indian companies that have borrowed in U.S. dollars or have exposure to foreign currency debt.
Read Also: Impact of Interest Rate Change on Financial Markets
Conclusion
To conclude interest rate and stock market share an inverse relationship. If you wish to receive consistent returns for a longer horizon is suggested. These short-term stances of rate change will create many complications. However, an investor should be well aware of the consequences of the rate change on the market so that he can make informed decisions. They should adopt a diversified investment strategy and take into account their own financial goals, and risk tolerance.
Frequently Answered Questions (FAQs)
How does interest rate affect bond prices?
Bond prices and interest rates have inverse relationships i.e., when the central bank increases the interest rates, bond prices decrease, and vice versa.
Do all stocks react to interest rate changes in a similar way?
No, stocks across sectors react differently to interest rate changes.
Who regulates and manages the interest rate in the stock market?
Reserve Bank of India controls and manages the interest rates.
Why does RBI increase the interest rate?
RBI increases the interest rates in order to control inflation and for the overall growth of the economy.
What happens to borrowing costs when RBI increases the interest rates?
Borrowing cost for the companies increases if RBI increases the rates.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.
Article History
Table of Contents
Toggle