| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Dec-13-23 | |
| Add new links | Nisha | Feb-27-25 | |
| Add new links | Nisha | Feb-27-25 |

- Blog
- lic case study business model and swot analysis
LIC Case Study: Business Model and SWOT Analysis

Everyone is familiar with LIC so much that for us, life insurance means LIC. But have you wondered what the business model of LIC is? How big is it, and how does it impact the insurance world?
In this case study, we will be answering such questions.
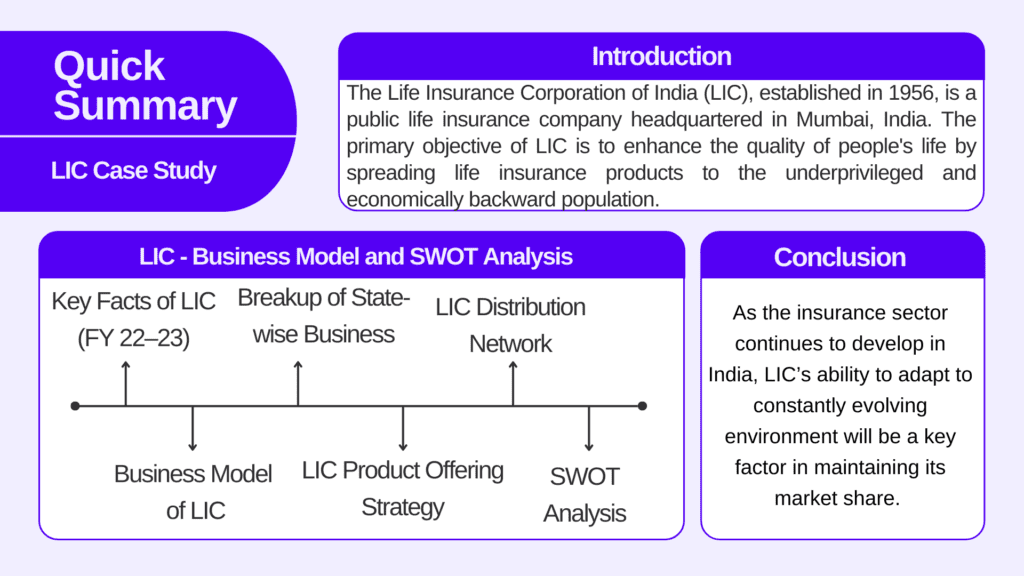
The Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), established in 1956, is a public life insurance company headquartered in Mumbai, India. The primary objective of LIC is to enhance the quality of people’s life by spreading life insurance products to the underprivileged and economically backward population.
LIC has six associate companies and seven subsidiaries. It ranks #1 among the insurance companies in India by size.
LIC went public in May 2022; however, only 3.5% of the equity is owned by the public and the rest 96.5% is owned by the promoter and promoter group, i.e., the government of India.
Read Also: Kotak Mahindra Bank: Business Model and SWOT Analysis
Key Facts of LIC (FY 22–23)
1. LIC is operating 2,048 branches and 1,580 satellite branches. In comparison, HDFC Life (major competitor) has only 467 branches.
2. LIC has overseas operations in 14 countries.
3. LIC has issued 27.74 crs. individual policies, assuring a sum of INR 5,868,481 crs.
4. In FY 22-23, LIC reported a net profit of INR 788,043 crs.
5. LIC has a market share of 71.76% in insurance policies.
Business Model of LIC
It’s simple: LIC sells insurance-related products to a wide range of customers. Consider the situation: you completed your graduation and were placed in a global MNC. Now, to secure your future, you’re looking for life insurance and get in touch with an insurance agent. The agent briefs you about all the current offerings. After analysing and trusting the brand value of LIC as Government of India backs it, you decided to go with LIC and bought life insurance from them.
Here, you’ll be giving money to LIC in the form of premiums on your policy for a period of time, say 10 years. LIC, in return, offers you financial benefits in case of unforeseen situations.
Now, LIC will invest this premium in various financial instruments: Stocks, Bonds, Mutual Funds, etc. In this situation, you are the only customer. As of September 2023, LIC has issued 27.74 crs. individual policies, assuring a sum of INR 5,868,481 crs. It’s a whopping number.
As of November 2023, they are managing assets worth INR 4,397,205 crs. which is close to the assets under management (AUM) of the entire mutual funds industry in India. Imagine how big LIC is!
Check out our blog to learn more about AUM: What is Asset Under Management (AUM) in Mutual Funds
Breakup of State-wise Business
| State | Market share (in%) |
|---|---|
| Maharashtra | 12% |
| West Bengal | 12% |
| Uttar Pradesh | 10% |
| Gujarat | 6% |
| Tamil Nadu | 6% |
| Karnataka | 6% |
| Rajasthan | 4% |
| Andhra Pradesh | 4% |
| Others | 39% |
LIC Product Offering
LIC offers numerous insurance plans to a broad range of customers, ranging from individuals to various groups (employers, institutions, etc.). It follows a customer centric approach and an efficient claim settlement process.
As of November 2023, LIC is offering more than 50 products ranging from insurance plans to health plans. It has an extensive distribution network of more than 1.2 million agents. Have a look at the chart below demonstrating the broad offering of LIC:
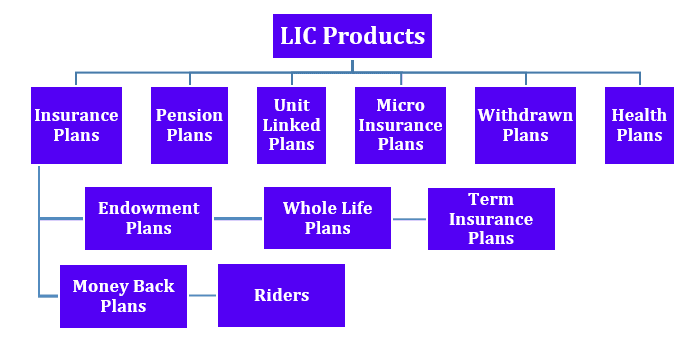
As you can observe from the above graph, LIC has a broad universe of offerings with insurance plans further divided into five categories:
- Endowment Plans: It is a participating plan which offers a combination of protection and savings.
- Whole Life Plans: Life insurance that provides financial protection throughout life.
- Term Insurance Plans: It is a life insurance that offers financial protection for a fixed period.
- Money Back Plans: It is a type of life insurance in which money is returned after a set period, in case of no contingency.
- Riders: These are add-on benefits purchased along with the insurance.
LIC Distribution Network
LIC has a vast distribution network, which sets it apart from its peers. As of March 2023, it has:
- 13.47 lakh individual agents and 160 corporate agents.
- 19,437 micro insurance agents.
- 3,628 branches and satellite offices.
- 295 brokers.
Read Also: Axis Bank Case Study: Business Model, Product Portfolio, and SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis of LIC

Strengths
- Brand Value: LIC is the oldest and largest insurance player in the industry, having a massive customer base. The brand value that LIC has created is a significant strength of it.
- Product Base: Its broad range of product offerings with a mix of participating and non-participating products is a huge advantage.
- Network: LIC has the largest force of insurance agents. The number has crossed 13 lakhs in FY 22-23. Further, LIC has 2,048 branches, 1,580 satellite branches, 19,437 micro-insurance agents and 295 brokers.
Weakness
- Lack of Online presence: LIC sells its policies via agents. It has an extensive network of agents all over India. However, the online presence of LIC is not up to the mark, and it heavily depends on insurance agents to sell its policies, which is a weak point in today’s digital world.
- Ineffective Advertising: LIC advertising falls short as compared to its competitors. One of the reasons that the LIC market’s share has been reduced in recent times.
- Lack of Innovation: Due to the massive size of LIC and red tape, it often lacks innovation and fails to diversify its products as per the evolving needs of the young generation.
Opportunities
- Market Size: There has been rapid growth in India in recent times, poverty is decreasing, and financial stability is increasing. With India’s massive population, LIC has an excellent opportunity to increase its market share.
- Online Services: LIC is an offline dominant business driven by its agents. There’s a great opportunity to expand its online presence.
- Increased Awareness: In India, financial awareness is increasing, which gives the opportunity to launch new products based on the demand of the evolving customers.
Threats
- Govt. Stake: LIC is a govt. owned entity where 97.5% of the stake is held by Govt. of India, operations of the LIC can be heavily influenced by it.
- Private Players: Tough competition from private players in the industry is a significant threat. In 2000, the Govt. of India allowed private players in the insurance industry and since then, the market share of LIC in insurance policies has kept on decreasing.
- Technological Challenges: There have been a lot of new developments in the fintech industry – digital lending, insurance, etc. However, if we look at LIC, it has a lot to do which poses a potential threat in an already declining market share.
Read Also: Paytm Case Study: Business Model and Marketing Strategy
Conclusion
LIC is a behemoth and the largest insurance player in India. It offers a wide range of insurance products, having an extensive distribution network. LIC’s massive portfolio also accelerated its income stream.
As the insurance sector continues to develop in India, LIC’s ability to adapt to constantly evolving environment will be a key factor in maintaining its market share. In other words, digital presence is essential in today’s world. The sharp decline has been seen in the operations of PSUs whenever government allowed private players in the industry. BSNL and Air India are flagship examples of this, but can LIC be an exception? Only time will tell.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who administers LIC?
The Ministry of Finance.
Who are LIC’s competitors?
LIC faces tough competition from HDFC Life, SBI Life, ICICI Lombard, etc.
What is a satellite office?
It is a kind of mini-office set-up by LIC in areas where no LIC branch available nearby.
What are participating and non-participating insurance policies?
In participating policies, one can enjoy the profits earned by the insurer, while in non-participating policies, there is no such provision.
When did LIC establish?
LIC was established in 1956.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.