| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Sep-23-24 | |
| Add new links | Nisha | Mar-01-25 |

- Blog
- mutual funds
- open ended
What is an Open-Ended Mutual Fund & How to Invest in it?

Ever wonder how you can make your money work for you and have liquidity? Well, open-ended mutual funds might be one solution to your issue. Open-ended mutual funds offer you the freedom to buy and sell shares at any time, giving you better control over your financial journey. But how do they work?
In this blog, we will discuss the basics of open-ended mutual funds, their advantages and disadvantages, and how they differ from close-ended mutual funds.
What are Open-Ended Mutual Funds?
An open-ended mutual fund is a pool of money invested in different securities, such as stocks, bonds, or other securities, on behalf of various individual investors. Unlike closed-ended funds, these mutual funds do not have a fixed number of shares, and investors can buy or sell shares at any time based on net asset value. This flexibility allows investors to enter and exit the fund according to their investment goals.

These funds are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions to achieve the fund’s objectives. Open-ended mutual funds can be used to implement various investment strategies, making them suitable for investors with different risk appetites and financial goals. Their liquidity and diversification help the investor build a robust portfolio while having access to his invested capital when needed.
How Do Open-Ended Mutual Funds Work in India?
Open Ended mutual funds follow the below process:
1. Investment Pooling: Investors invest in the mutual fund by adding money to the mutual fund’s investment pool. Each investor’s money is combined with money from the other investors to form a corpus or a pool of money.
2. Portfolio Management: The fund managers invest the pooled money in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other securities based on the fund’s investment objectives.
3. Net Asset Value Calculation: The NAV of the fund is computed on a daily basis. It represents the net asset value of a fund per unit after accounting for its liabilities. The NAV is used to calculate the price at which buying or redemption of units takes place.
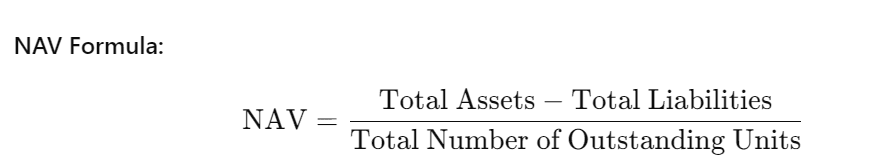
4. Buying and Redeeming Units: Investors buy or redeem the fund’s units at the price set by the NAV.
5. Dividends and Distributions: Any income in the form of dividends or interest is distributed among investors and can be reinvested to buy additional units.
6. Performance Monitoring: The fund manager continuously monitors the fund’s performance and rebalances the portfolio according to the fund objectives. The investors may monitor the fund’s performance through various reports and updates.
In India, open-ended mutual funds fall under the purview of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which assures transparency and protection of investors.
How to Invest in Open-Ended Mutual Funds?
Investors can invest in an open-ended mutual fund in two ways:
- During the NFO period: Investors can invest during the New Fund Offer (NFO) period and are allotted units based on par value or face value.
- After the NFO period: Investors can buy units of open-ended mutual funds at NAV after the NFO period.
Moreover, an investor can redeem mutual fund units at NAV at any time. However, ELSS is an exception as it has a lock-in period of three years, after which the investor can sell the units just like any other open-ended scheme.
Read Also: History of Mutual Funds in India
Advantages of Open-Ended Mutual Funds
The advantages of open-ended mutual funds are:
- Liquidity: There is a high level of liquidity because investors can purchase or redeem units at the NAV on any business day.
- Diversification: It pools money from many small investors to form a diversified portfolio, reducing the investment risk of individual investments.
- Professional Management: Professional fund managers invest in pooled funds, which is beneficial for people who do not have much time or expertise in making investment decisions.
- Regular Updates: Since NAV is calculated on a daily basis, investors get regular updates about their investments.
- Flexibility: The investors can invest a small amount of money periodically or even make a lump sum investment. This makes open-ended mutual funds suitable for various kinds of financial goals.
Disadvantages of Open-Ended Mutual Funds
Disadvantages of open-ended mutual funds are:
- Market Risk: The value of investments in open-ended mutual funds may vary with market conditions, which can result in potential losses.
- Management Fees: Mutual funds charge management fees, which reduces returns.
- No Control Over Individual Investments: The investor has no say in the selection of securities or any other investment decision.
- Potential for Lower Returns: Depending on the fund’s strategy and the prevailing market conditions, returns may be lower compared to direct investment in individual securities.
- Redemption Pressure: Open-ended mutual funds must maintain a cash reserve to meet redemption requests, which reduces the overall returns.
Difference Between Open-Ended and Close-Ended Mutual Funds
| Parameters | Open-Ended Mutual Funds | Closed-Ended Mutual Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Buy and Redeem | Shares can be bought or redeemed at NAV on any business day. | Investors can subscribe to close-ended mutual funds only during the NFO period or can buy and sell shares on the stock exchange. |
| Liquidity | Open-ended mutual funds have high liquidity. | Close-ended mutual funds have low liquidity. |
| Fund Size | The fund size varies because investors can invest or redeem shares at any time. | The fund size is fixed and remains constant throughout its life. |
| Pricing | Price is based on the Net Asset Value (NAV). | Price is based on the demand and supply of units traded on the stock exchange. |
| Ways to Invest | Investors can invest in open-ended mutual funds via SIP or make a lump sum investment. | Investors can invest only lump sum amounts in close-ended mutual funds. |
Conclusion
In summary, open-ended mutual funds provide flexibility, liquidity, and professional management and, hence, are an apt solution for investors seeking diversification and easy redemptions. On the other hand, investors pay management fees and are exposed to market risks. The closed-ended mutual funds have fixed fund sizes with lower liquidity. Knowing the differences helps investors select funds according to their financial goals. It is advised to consult a financial advisor before investing.
| S.NO. | Check Out These Interesting Posts You Might Enjoy! |
|---|---|
| 1 | What Is An IPO Mutual Fund? Should You Invest? |
| 2 | Mutual Fund Taxation – How Mutual Funds Are Taxed? |
| 3 | What is Solution Oriented Mutual Funds? |
| 4 | What is TREPS & Why Mutual Funds Invest in it? |
| 5 | Debt Mutual Funds: Meaning, Types and Features |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How frequently does an open-ended mutual fund update its NAV?
The NAV is calculated and updated daily, reflecting the current value of the fund’s portfolio.
Do open-ended mutual funds offer diversification?
Yes, they invest in a diversified portfolio of assets, reducing the risk associated with investment in a single security.
Can I redeem my investment from an open-ended mutual fund at any time?
Yes, you can redeem your units at the current NAV.
How are open-ended mutual funds regulated in India?
Open-ended mutual funds are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India, ensuring transparent operations and the safety of investor capital.
Are open-ended mutual funds suitable for a short-term investment horizon?
Open-ended mutual funds are suitable for a short-term investment horizon as they have high liquidity. However, inventors must assess the fund’s investment objectives and strategy before investing.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.