| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Dec-15-23 | |
| Add internal links | Nisha | Mar-12-25 |

- Blog
- risk management in trading meaning uses and strategies
Risk Management In Trading: Meaning, Uses, and Strategies
First, we need to understand what is risk and the factors that create risk in the stock market before we learn about risk management.
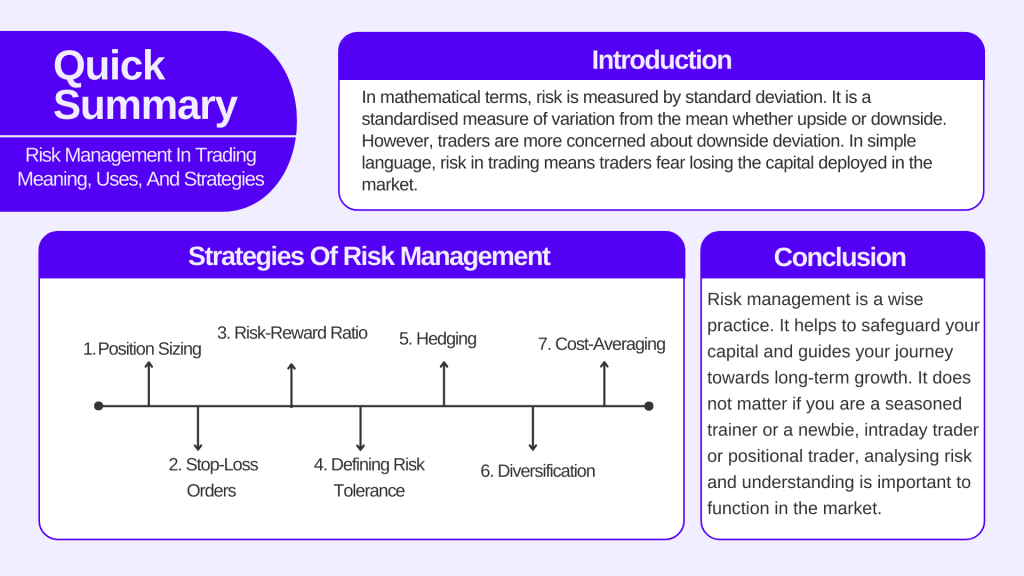
In mathematical terms, risk is measured by standard deviation. It is a standardised measure of variation from the mean whether upside or downside. However, traders are more concerned about downside deviation. In simple language, risk in trading means traders fear losing the capital deployed in the market.
Various factors like market fluctuations, interest rate changes, volatility, and poor financial results can cause risk.
What is Risk Management?
Risk management is considered a cornerstone for effective trading. It involves identifying, analysing and mitigating potential risks in capital preservation while trading and achieving long-term success.
Traders, when trading in stocks, commodities, currencies, or any kind of financial instrument, implement different risk management strategies to control and minimise the losses incurred on their capital.
Effective risk management helps the trader to make informed trading decisions, help overcome fear and greed, and generate better returns.
Strategies of Risk Management
1. Position Sizing
Position sizing means determining the capital allocation on a particular trade depending on the total capital and risk appetite.
2. Stop-loss Orders
Setting pre-defined stop loss orders while trading not only automatically exits your positions but also reduces risk and minimises potential losses. You can trail your stop loss which means that you can modify your stop loss based on the changes in prices of the stock.
3. Risk-Reward Ratio
Aim for trades with risk-reward ratios greater than 1:1, meaning potential profit outweighs loss and try focusing on trading opportunities with limited downside potential.
4. Defining risk tolerance
Before entering into a trade, do not forget to define the maximum loss you can afford if a security slips into losses. Risk tolerance is generally based on your financial goals. Avoid taking excessive risks.
5. Hedging
Hedging is defined as a financial strategy that traders and investors use to protect their portfolios. It offsets losses with gains by taking an opposite position in the financial instrument you are trading.
6. Diversification
Remember the famous saying, “Do not put all your eggs in one basket”. Do not concentrate your capital on a single stock or financial asset. Diversification of the portfolio is crucial to avoid over-exposure to risks.
7. Cost-Averaging
When averaging the stocks, you buy them at different low prices at regular intervals. This helps in managing the price risk.
Read Also: What is Carry Trade? Definition, Example, Benefits, and Risks
Algorithmic Trading & Risk Management
Algorithmic Trading, also known as algo trading, involves the usage of computer algorithms to execute trades.
No doubt that algorithmic trading in recent times has been revolutionary since it provides traders with speed, automation, efficiency, and no human bias while executing trades. However, it comes with risk and can amplify your losses. Therefore, it is necessary to manage the risk caused by algo trading.
Strategies for risk management are more or less similar for manual and algorithmic trading. In addition to the above-mentioned strategies, other points that a trader needs to focus on are as follows:
1. Conduct thorough back testing to analyse the past performance of the algorithm that you are using. Try implementing the strategies in different and extreme market conditions to ensure proper working. This will help you identify potential risks.
2. Do work on failover mechanisms to manage technical failures and analyse how the algo will react in such situations.
3. Regularly monitor algorithm performance, track risk metrics, and adapt strategies as needed.
Trading Psychology and Risk Management

Trading psychology and risk management are two important pillars of successful trading, intricately woven together like the warp and weft of a well-made fabric. You need to control your emotions to implement effective risk management.
Phycological factors like overconfidence, greed, and fear of loss can lead to poor risk management and impulsive decisions. Identifying your emotional triggers can help you manage your losses and mitigate the risks involved.
You need to train your mind and develop a plan while trading in the markets and cultivate the discipline to stick to your trading plan so that you can achieve long-term success.
Remember that trading psychology and risk management are ongoing processes that you need to continuously learn to refine your strategies and do not forget to seek professional advice to get valuable insights about the market.
Risk Management for Day Traders
Risk management is necessary for intra-day traders since they carry out several daily trades. This increases the chances of losses. Therefore, day traders should stick to their pre-determined risk limit and avoid overtrading.
Developing a trading plan that defines the entry/exit point for your trades can help the day-traders in risk management. If a day trader wishes to manage the risk, he or she must be particular with leverage. Leveraging can lead to an increased risk of losses.
Identify and trade with the prevailing trend. This can improve the probability of success and reduce the likelihood of being on the wrong side of a significant move. Do not trade just because you incurred a loss in your previous trade. Revenge trading often led to losses.
Risk Management – Forex and Options Trading
The above-mentioned strategies for risk management work well with forex and options trading.
But forex trading, with its high leverage and 24/7 market access, carries significant risks. By implementing the strategies discussed above and using technical analysis to understand the market trends, you can execute proper risk management to preserve your capital.
In the case of Options trading, apart from the above-listed points, additional areas to keep in mind so that the risk can be managed are
1. Aiming for delta-neutral positions to minimise exposure in direction trades.
2. Use credit spreads like bull call spreads or bear put spreads to reduce the exposure.
3. You should be aware of the effect of implied volatility on the prices of the option and adjust your positions accordingly.
4. Options lose their value with time because of theta decay. One must adjust position size and expiry dates accordingly to manage the risk.
Read Also: What is Price Action Trading & Price Action Strategy?
Conclusion
On a parting note, risk management is a wise practice. It helps to safeguard your capital and guides your journey towards long-term growth. It does not matter if you are a seasoned trainer or a newbie, intraday trader or positional trader, analysing risk and understanding is important to function in the market.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach. Your risk management plan should be personalised as per your risk tolerance and capital availability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is risk management?
Risk management involves identifying, analysing and mitigating potential risks in capital preservation while trading and achieving long-term success.
What are some common risk management strategies?
Some common risk management strategies are position sizing, hedging, stop loss orders, etc.
Why risk management is important for traders?
Risk management is important for traders since it helps in minimising losses and capital preservation.
What is position sizing?
Position sizing means determining the capital allocation on a particular trade depending on the total capital and risk appetite.
Is risk management the same for all traders?
Risk management is not the same for all traders because it depends on individual trading style and capital.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.