| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Sep-13-24 | |
| Infographic Update | Ranjeet Kumar | Apr-03-25 | |
| Infographic Update | Ranjeet Kumar | Apr-03-25 | |
| Add new links | Nisha | Apr-11-25 | |
| Added Case Study PDF & PPT | Ranjeet Kumar | Apr-16-25 |

- Blog
- state bank of india case study
SBI Case Study: India’s Leading Public Sector Bank


Download pdf
Download ppt
For over two centuries, the SBI has been a giant in the Indian banking industry, playing a pivotal role in the country’s financial development. As one of the largest banks in India, it has not only promoted economic development but also catalyzed financial inclusion, reaching even the most remote corners of the country. Its commitment to innovation and technological advancements has transformed the way banking is conducted.
In today’s blog, we will explore the services offered by SBI and do a SWOT analysis to understand its position in the competitive market and recognize possible areas of growth and development.
SBI Company Overview
SBI is India’s largest public sector bank and a titan in the Indian banking landscape with a 1/4th market share. SBI is headquartered in Mumbai and holds a rich heritage of over 200 years.
The roots of SBI trace back to 1806 when the Bank of Calcutta was established, the first joint stock bank in British India. Three separate presidency banks, Bank of Bengal, Bank of Bombay, and Bank of Madras, emerged across British India. In 1921, the three presidential banks merged to form the Imperial Bank of India.
In 1955, the government of India nationalized the Imperial Bank of India and renamed it the State Bank of India. SBI later acquired various state-associated banks and commercial banks.
SBI has played an important role in bringing banking services to rural areas. Currently, SBI has a strong network of 22,405 branches and 65,627 ATMs.
The Bank’s core values are Service, Transparency, Ethics, Politeness, and Sustainability.

Business Model & Services Provided by SBI
SBI caters to a wide range of customers and offers a comprehensive suite of financial products and services. These services can be broadly classified into:
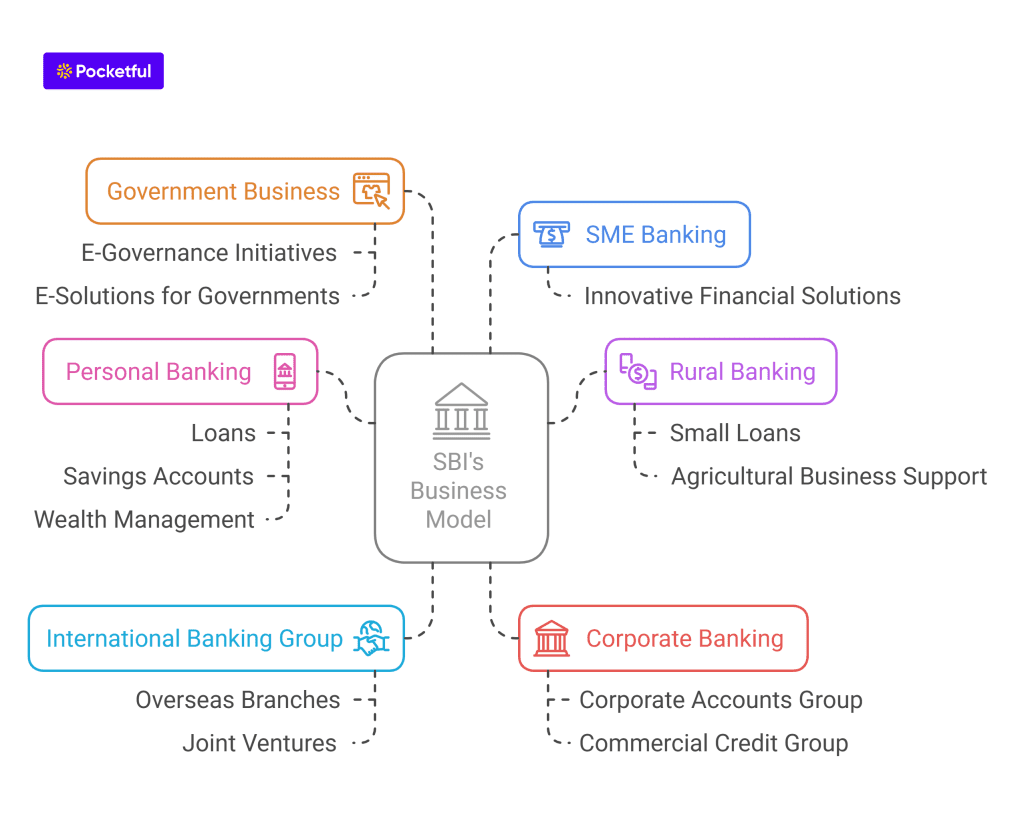
- Personal Banking – Under this segment, the bank offers services such as loans, savings accounts, current accounts, digital loans, NRI business, and wealth management.
- Rural Banking – Under this segment, the bank helps rural people of India by providing financial services, small loans, and agricultural business support.
- International Banking Group – Overseas branches, banking subsidiaries, joint ventures, and associates are consistently paving the way in international banking in India.
- SME Banking – The bank offers innovative financial solutions to its SME client base under this segment.
- Corporate Banking – Top corporations in the nation, including Navratna PSUs, can choose from a wide range of financial products and services provided by the bank’s Corporate Accounts Group and Commercial Credit Group.
- Government Business – The bank helps the government of India with e-governance initiatives and creates e-solutions for both Central and State Governments.
Read Also: Punjab National Bank vs State Bank of India
Financial Statements of SBI
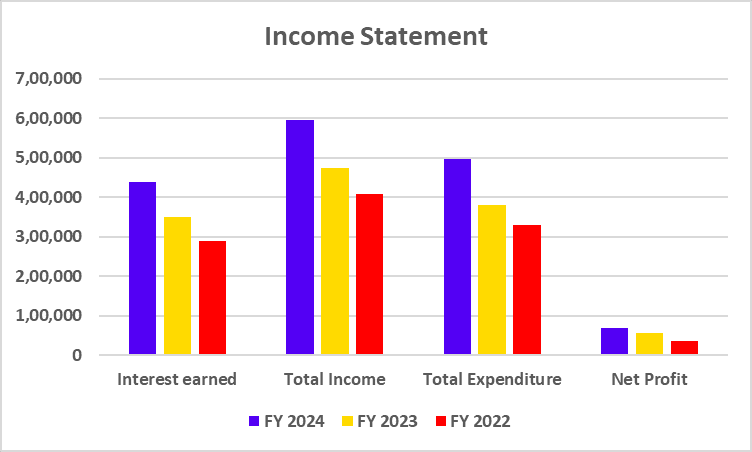
Income Statement
| Particulars | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interest earned | 4,39,188 | 3,50,844 | 2,89,972 |
| Total Income | 5,94,574 | 4,73,378 | 4,06,973 |
| Total Expenditure | 4,95,543 | 3,79,744 | 3,30,519 |
| Net Profit | 68,224 | 56,609 | 36,395 |
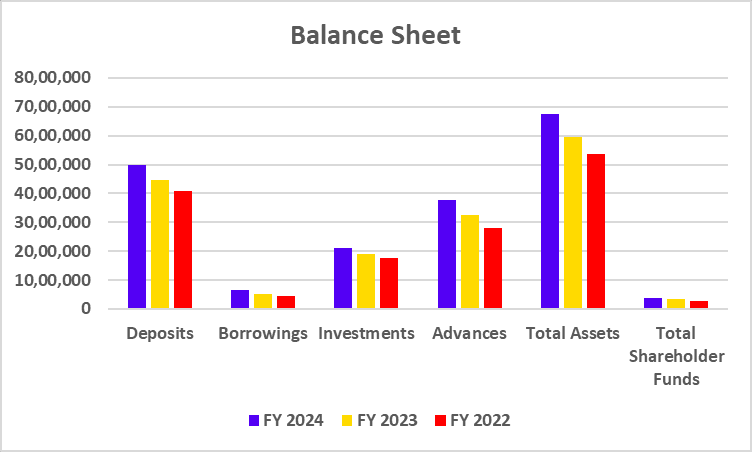
Balance Sheet
| Particulars | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deposits | 49,66,537 | 44,68,535 | 40,87,410 |
| Borrowings | 6,39,609 | 5,21,151 | 4,49,159 |
| Investments | 21,10,548 | 19,13,107 | 17,76,489 |
| Advances | 37,84,272 | 32,67,902 | 27,94,076 |
| Total Assets | 67,33,778 | 59,54,418 | 53,60,883 |
| Total Shareholder Funds | 3,86,491 | 3,30,282 | 2,81,317 |
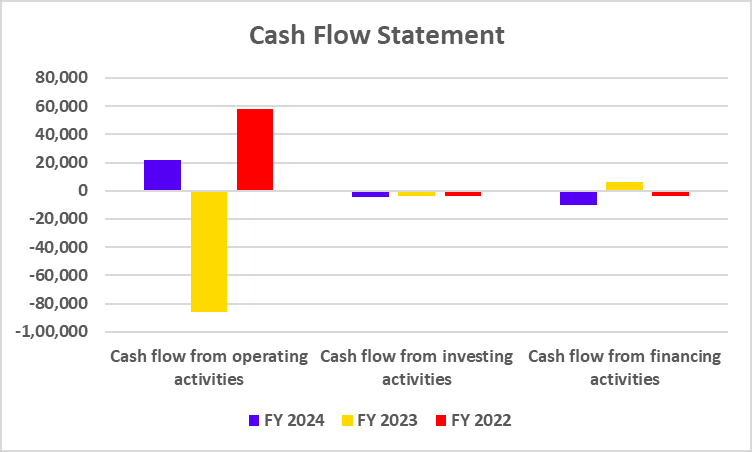
Cash Flow Statement
| Particulars | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash flow from operating activities | 21,632 | -86,013 | 57,694 |
| Cash flow from investing activities | -4,251 | -4,040 | -3,618 |
| Cash flow from financing activities | -9,896 | 6,386 | -3,844 |
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
| Particulars (in %) | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Net Interest Margin | 2.66 | 2.70 | 2.49 |
| Net Profit Margin | 15.51 | 16.12 | 12.53 |
| ROE | 17.31 | 16.80 | 12.53 |
| ROCE | 1.63 | 1.74 | 1.57 |
| CASA | 39.92 | 42.66 | 44.51 |
SWOT Analysis of SBI
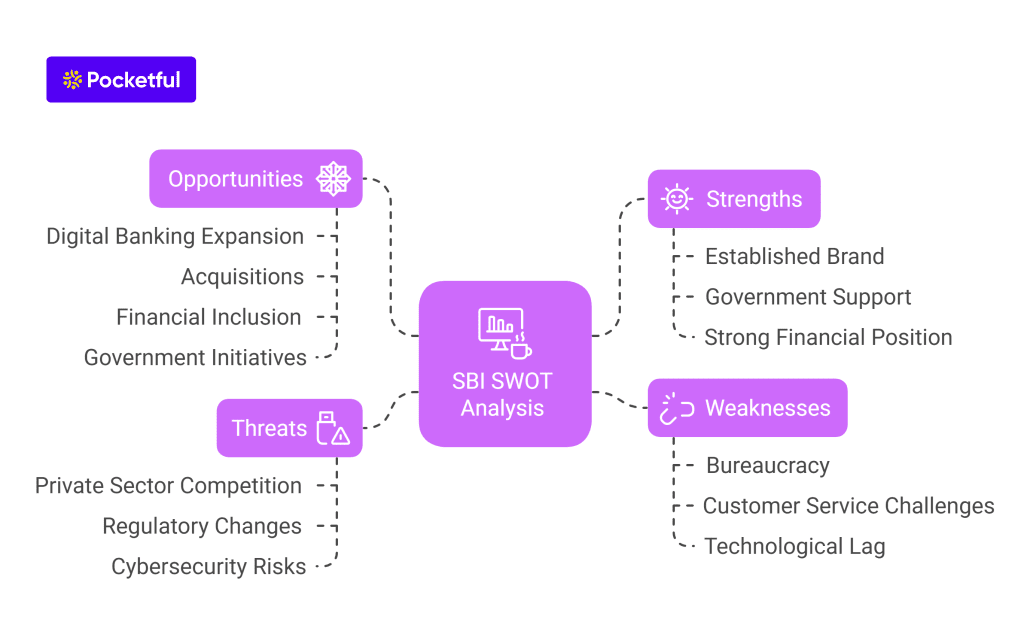
Strengths
- SBI is a trusted and established brand in India that is known for its reliability and long history.
- It benefits from government support as a public sector bank, which can be beneficial in terms of policy benefits and stability.
- The bank holds a strong financial position, which allows it to grow and expand.
Weaknesses
- SBI’s large size and public sector status can affect bank operations due to bureaucracy and slow decision-making.
- Although the bank has made strong progress in enhancing its customer service, it continues to encounter obstacles in ensuring a superior customer experience.
- It has been lagging behind certain private sector banks when it comes to embracing new technologies and digital innovations.
Opportunities
- The increasing use of digital banking is an opportunity for SBI to offer more online and mobile banking services.
- SBI could consider buying smaller banks or financial institutions to improve its market position.
- It could also focus on reaching rural populations, women, and small businesses to encourage financial inclusion.
- SBI can also benefit from government initiatives such as Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana and Mudra Yojana.
Threats
- Private-sector banks increasingly provide competitive products and services and are often quicker to embrace advanced technologies and digital innovations.
- SBI’s operations could face challenges because of government or regulatory changes, and sticking to complex regulatory requirements can be time-consuming and costly.
- Cyberattacks and data breaches are becoming more prevalent, posing an ever-growing risk and having the potential to cause financial losses in addition to undermining the bank’s reputation.
Read Also: SBI Cards and Payment Services Case Study: Products, Financials, and SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
The SBI stands out as a top-tier public sector bank in India, underpinned by its extensive network, government support, and wide range of products and services. Nevertheless, there are considerable challenges, economic uncertainties, and competition in the Indian banking industry. To prosper in the future, SBI must concentrate on digital transformation, financial inclusion, international expansion, innovation, and risk management. The bank has the opportunity to maximize its strengths and overcome its weaknesses, ensuring its indispensable position in the Indian economy and delivering financial solutions to its customers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is SBI a government bank?
Yes, SBI is a public sector bank.
Does SBI also offer investment products?
SBI offers investment products such as mutual funds, fixed deposits, and government bonds, apart from regular banking services.
How is SBI adapting to the digital age?
SBI is investing in digital banking initiatives to improve customer experience and efficiency.
Does SBI offer NRI banking services?
Yes, SBI offers a range of NRI banking services to Indian citizens living abroad.
Should I invest in SBI?
Investing in SBI depends on an individual’s risk profile and financial objective. Remember, investing involves risk, and there is no guarantee of returns. It is important to consult your financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.