| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Mar-13-24 | |
| Update Content | Nisha | Mar-24-25 | |
| Infographic Update | Ranjeet Kumar | Apr-03-25 |

- Blog
- tata motors case study history business model products financials peers and swot analysis
Tata Motors Case Study: Business Model, Financials, and SWOT Analysis
From the streets of Mumbai to the prestigious avenues of London, the growls of Tata Motors engines echo across the globe. This Indian automotive giant has come a long way, evolving from a locomotive manufacturer to a diverse automobile powerhouse.
In today’s blog, we will delve into the world of this fascinating company from exploring its rich history to ambitious plans.
All About Tata Motors
Tata Motors is India’s 3rd largest automobile company and is a leading global manufacturer of cars, utility vehicles, buses, trucks, and defence vehicles. Tata Motors was incorporated in the year 1945 and was a part of the Tata Group which was founded by Jamshedji Tata in the year 1868.
Some of the world’s most iconic brands, including Jaguar Land Rover in the UK and Tata Daewoo in South Korea are a part of the automotive operations of the group.
Tata Motors is committed to developing innovative and sustainable vehicles for the future of mobility. The company operates on a philosophy of ‘giving back to society’.
Additionally, in a major push for clean transportation, Tata Motors signed a deal to supply 3,500 EVs to BluSmart Mobility, India’s first electric and shared smart mobility company, expanding Delhi NCR electric fleet and offering customers more environment-friendly travel options.
History of Tata Motors
The Tata Motors history dates back to 1945. Tata Motors was founded as Tata Engineering and Locomotive Company (TELCO), which initially focused on locomotives.
The company entered the commercial world market in the year 1954 through a joint venture with Daimler-Benz, establishing India’s first heavy vehicle manufacturing facility. Gradually it expanded the commercial vehicle portfolio with trucks and buses, becoming a dominant player in the market.
2008 marked a turning point with the acquisition of Jaguar and Land Rover from Ford, propelling Tata Motors onto a global stage.
Did You Know?
In the year 1991, India’s first sports utility vehicle (SUV), Tata Sierra, was designed and manufactured by Tata Motors.
Highlights (FY 2022-23)
- Presence in more than 150 countries.
- ₹ 29,398 crores was spent on research and development.
- 25 manufacturing facilities, 9 R&D centres and 3 Design labs.
- 91,811 collective workforces.
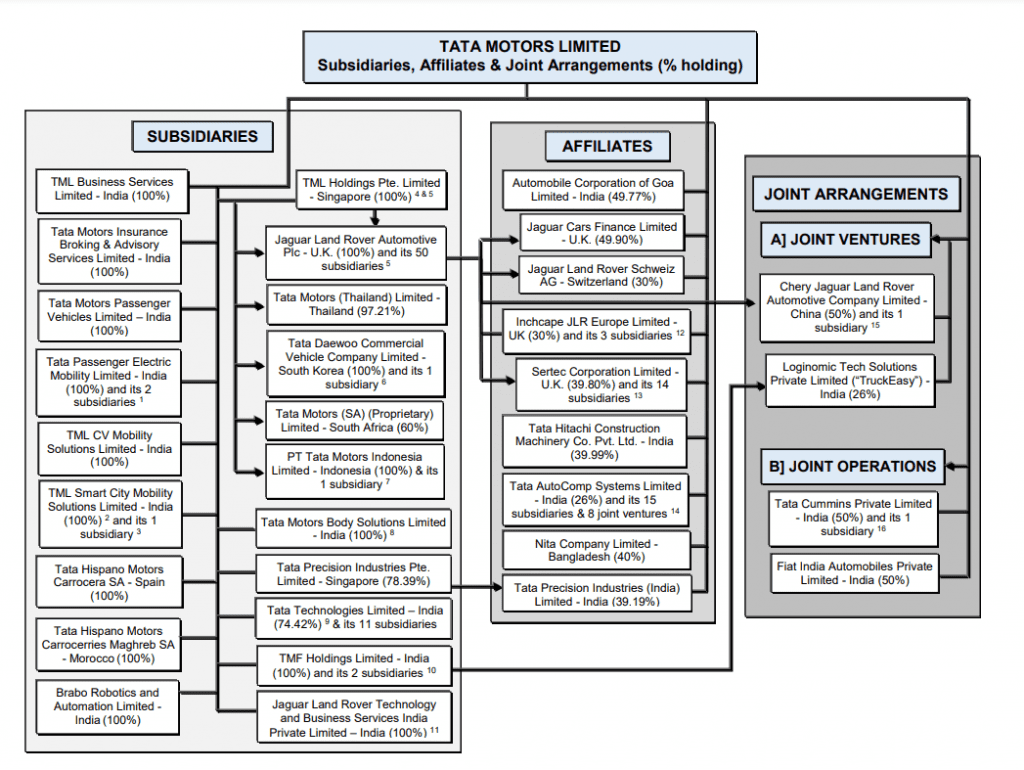
Subsidiaries of Tata Motors
Some of the subsidiaries of Tata Motors is mentioned below:
- Tata Motors Passenger Vehicles Limited: TMPV is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Tata Motors and leads the passenger vehicle business in India. The company offers a diverse range of sedans, SUVs, and electric vehicles.
- Tata Passenger Electric Mobility Limited (TPEM): TPEM was established in FY 2021-22 to carry out the Passenger Electric Mobility Business with a funding of INR 7500 crore from TPG Rise. The company aims to channel future investments into electric vehicles.
- Jaguar Land Rover (JLR): JLR, a well-known British manufacturer of luxury cars, was acquired by Tata Motors in 2008. The company exemplifies quality and sustainability.
- Tata Motors Finance Limited (TMFL): TMFL and Tata Motors Finance Solutions Limited (TMFSL) are TMF Holdings Limited (TMFHL)’s Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) subsidiaries. TMFHL is a Core Investment Company (CIC) and Tata Motors’ completely owned subsidiary. TMFL provides vehicle financing solutions to Tata Motors customers in India.
Business Model of Tata Motors
he Tata Motors business model integrates manufacturing, R&D, global sales, financial services, and innovation to position itself as the most aspirational brand in India’s automotive industry.
Tata Motors holds 10 manufacturing facilities, and 3 R&D/engineering and design centres. Furthermore, there are 12 worldwide manufacturing and engineering facilities for JLR.
The company aims to become the most aspirational brand in the Indian Automotive Industry.
Full range of activities that TML provides includes manufacturing operations, logistics, financial services, global sales network, customer service network, mobility service, innovation and technology, design and engineering, and strategic sourcing.

Product Portfolio of Tata Motors
The existing Commercial Vehicle Range of the company is as follows
MHCV, Buses and Vans, ILCV, SCV and PICKUP.
Last but not least the showstopper in the CV range is the ACE EV which features TML’s EVOGEN powertrain.
The existing Passenger Vehicle Range includes products like Tiago, Tigor, Altroz, Punch, Nexon, Harrier, and Safari.
Existing Electric Vehicle Range includes Tiago EV, Tigor EV, XPRES-T EV, Nexon EV, and NEXON EV MAX.
Also, the company boasts that the EV contribution is likely to increase to 25% in 5 years and reach 50% by 2030.
Apart from the portfolio mentioned above, TML offers a luxury range as well which includes Jaguar and Land Rover, the two distinct British brands with a rich heritage design.
Did you Know?
Tata Motors’ first indigenously developed passenger car, Tata Indica was presented in 1998 at the Geneva Motor Show.
Market details of Tata Motors
| Current Market Price | ₹ 716 |
| Market Capitalization (in ₹ crores) | 2,63,536 |
| Book Value | ₹ 275 |
| 52-Week High/Low | ₹ 1,179 / 606 |
| Face Value | ₹ 2 |
| Return on Equity | 49.4 % |
| Stock P/E | 8.33 |
Financial Statement Analysis
Income Statement
| Key Metrics | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Income | 4,43,877 | 3,50,600 | 2,81,507 |
| Total expenses | 4,06,636 | 3,37,717 | 2,79,198 |
| EBIT | 37,241 | 13,283 | 2,308 |
| Net Profit | 31,106 | 2,353 | -11,234 |
(Above mentioned figures are in ₹ crores unless stated otherwise)
Balance Sheet
| Key Metrics | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Assets | 1,68,392 | 1,51,528 | 1,46,978 |
| Non-Current Assets | 2,02,272 | 1,84,553 | 1,83,642 |
| Current Liabilities | 1,73,617 | 1,55,027 | 1,50,683 |
| Non-Current Liabilities | 1,01,405 | 1,25,955 | 1,31,105 |
| Total Shareholder Funds | 87,464 | 47,819 | 44,555 |
(Above mentioned figures are in ₹ crores unless stated otherwise)
Cash Flow Statement
| Key Metrics | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash Flow from Operating Activities | 67,915 | 35,388 | 14,282 |
| Cash Flow from Investing Activities | -22,828 | -16,804 | -4,775 |
| Cash Flow from Financing Activities | -37,005 | -26,242 | -3,380 |
(Above mentioned figures are in ₹ crores unless stated otherwise)
Peer Comparison
| Company | Current Market Price (in ₹) | Market Capitalization (in ₹ crores) | P/E | ROCE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tata Motors | 716 | 2,63,536 | 8.33 | 20.1 |
| Ashok Leyland | 212 | 62,210 | 22.3 | 15 |
| Olectra Greentec | 1,264 | 10,374 | 78.8 | 14.8 |
| Force Motors | 8,845 | 11,655 | 23 | 23.8 |
| SML ISUZU | 1,750 | 2,532 | 20.9 | 23.6 |
Read Also: Tata Power Vs Adani Power: Comparison Of Two Energy Giants
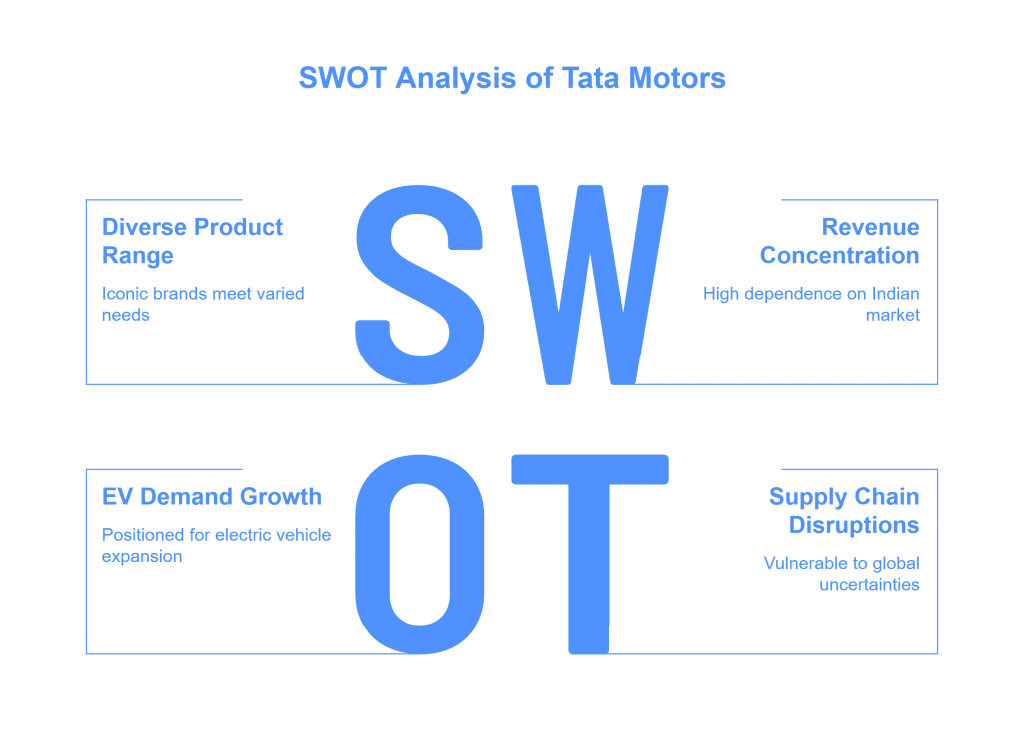
SWOT Analysis of Tata Motors
Strengths
- The company offers a diverse range of product portfolios including iconic brands like JLR which cater to the needs of a wide range of customers.
- Consistent investments in strategic partnerships and collaborations to infuse new technologies help the company expand its business operations.
- The company considers the quality and safety of the customers as key parameters while manufacturing products.
- Tata Motors invests heavily in research and development and tries to curate future-ready vehicles with features like electric mobility and connectivity.
- They actively promote sustainable practices through electric vehicles and emission reduction initiatives aligning with environmental concerns.
Weaknesses
- A significant portion of its revenue comes from India, which exposes the company to economic fluctuations and regulatory changes in the country.
- Despite the pervasiveness of JLR, their presence in major global markets like China and North America remains limited.
- Dependence on imported materials exposes the company to price fluctuations, impacting the profit margins.
- The EV industry is dynamic as it changes quickly, failure to keep up with market trends may affect margins.
Opportunities
- Tata Motors is well-positioned to capitalise on the rising demand for electric vehicles with their existing offerings and future developments.
- Consistent investments in research and development can lead to breakthroughs in areas like autonomous driving and connected cars, offering a competitive advantage.
- Government initiatives promoting EVs can create favourable market conditions for Tata Motors.
- They can leverage JLR to further expand their reach in international markets.
Threats
- Any kind of disruption in the supply chain can affect business operations.
- The company is exposed to several global economic and geopolitical situations such as wars, natural disasters, and pandemics.
- Sudden shifts in policy and environmental regulations can disrupt operations.
- Rapid advancements in technology can make existing products obsolete if they are not constantly updated.
- Brand positioning is a challenge in a dynamic automotive market with more intense competition from existing OEMs and new entrants in the market.
Growth of Tata Motors
Tata Motors has indeed seen incredible growth in the Indian domestic market, especially in the commercial vehicle segment. Rising GDP and infrastructure spending can further boost the demand for commercial vehicles. New models such as Tiago, Nexon, and Harrier have been well-received by customers. Additionally, the company has captured the growing market segments with the latest designed EVs.
Conclusion
Tata Motors stands as a prominent player in the Indian automotive landscape, with a diversified product portfolio, strong brand recognition and a commitment to innovation and sustainability. Their business model positions them well for future growth. However, navigating and addressing key challenges will be critical for the company.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is electric mobility a big focus for TML?
With India’s growing environmental concerns and rising fuel costs, electric vehicles represent a good solution.
Can Tata Motors become a global leader in the automotive industry?
The question cannot be answered yet but capitalising on opportunities will be important for them to compete on a global scale.
What are the latest innovations of the company?
TML is investing in connected car technology, autonomous driving, and many other revolutionary innovations.
Which company made the world’s cheapest car?
The iconic Tata Nano was the cheapest car ever sold and was produced with the objective of providing affordable mobility to people.
Does the company focus majorly on budget cars?
Tata Motors fulfil the diverse needs of customers by offering premium vehicles like Land Rover Discovery and budget friendly cars like Tata Punch.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.