| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Aug-05-24 | |
| Add new links | Nisha | Apr-14-25 |

- Blog
- tata steel case study
Tata Steel Case Study: Business Model, Financial Statements, SWOT Analysis
India has done remarkably well since gaining independence to develop its infrastructure, including its buildings, ports, and railroads. Steel is the primary material utilized in all infrastructure-related activities. An Indian corporation founded before the nation’s independence manufactures essential raw materials like steel.
In today’s blog post, we will present a case study on Tata Steel Limited, financial statements and do a SWOT analysis.
Tata Steel Company Overview
The renowned Indian businessman Mr Jamsetji Tata established Tata Iron and Steel Company Limited (TISCO) in 1907 and was later renamed Tata Steel Ltd. in 2005. The firm established its first facility and began producing steel in 1912. The business provided steel to the defense sector during the Second World War. In 2004, the business bought Singapore-based NatSteel Holdings to broaden its global presence. The company has since completed several domestic and foreign acquisitions. The most recent occurred when it bought Bhushan Steel Limited in 2018. The company’s headquarters are in Mumbai.
Business Model of Tata Steel
Tata Steel’s business model is diversified and robust, encompassing the entire steel value chain. Owning coal and iron ore mines in India ensures a steady supply of raw materials, while steel factories in Europe and India strengthen its global presence. Leveraging cutting-edge technologies, Tata Steel enhances product innovation and efficiency. Notably, the Tata Steel business model significantly impacts India’s economy, contributing nearly 4% to the GDP annually.
Product Portfolio of Tata Steel
The company provides hot rolled, cold rolled, coated coil, tubes, rebar, and wire rods to various industries such as automotive, construction, consumer goods, agriculture, etc. Long steel products, including wire, rod, rail and bars, are utilized to build railroads and infrastructure. Flat products are used in the manufacturing of consumer durables and automobiles. In addition, they offer related goods like steel-coated and stainless steel products.
Market Data of Tata Steel Limited
| Current Market Price | INR 158 |
| Market Capitalization | INR 1,97,302 crores |
| 52 Week High | INR 184 |
| 52 Week Low | INR 114 |
Financial Statements of Tata Steel
Income Statement
| Particulars | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Revenues | 2,30,979 | 2,44,390 | 2,44,744 |
| Total Expenditure | 2,24,561 | 2,20,274 | 1,89,704 |
| Net Profit | -4,851 | 7,657 | 41,100 |
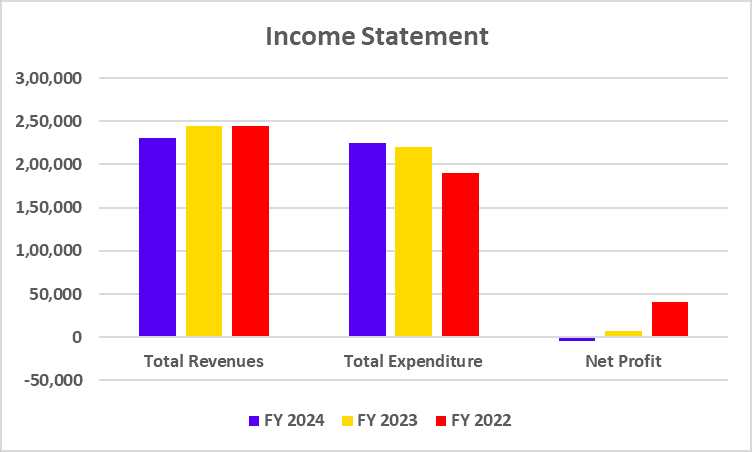
The above graph clearly shows that the company’s revenue from operations has decreased, which has directly impacted the company’s net profit.
Balance Sheet
| Particulars | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Assets | 70,548 | 86,665 | 92,556 |
| Total Assets | 2,73,423 | 2,88,021 | 2,85,445 |
| Current Liabilities | 98,403 | 97,295 | 90,588 |
| Total Shareholder Funds | 92,035 | 1,03,082 | 1,14,443 |
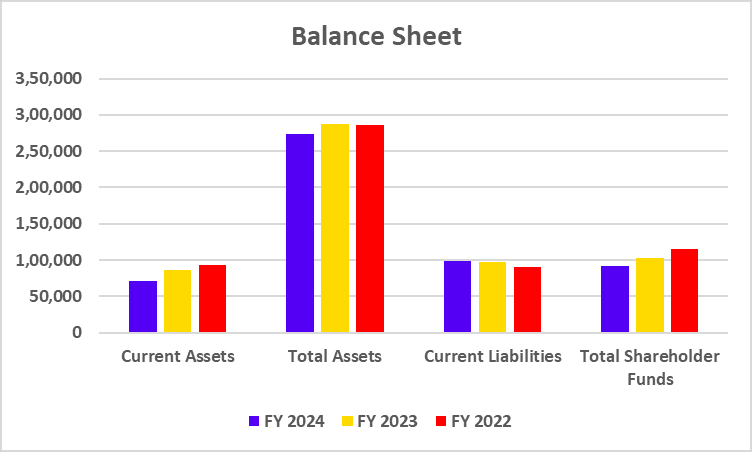
Based on the above table, we can conclude that the company’s current assets have decreased over time, whereas its current liabilities have increased.
Cash Flow Statement
| Particulars | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Net Cash flow from Operating Activities | 20,300 | 21,683 | 44,380 |
| Net Cash flow from Investing Activities | -14,251 | -18,679 | -10,881 |
| Net Cash flows from Financing Activities | -11,096 | -6,980 | -23,401 |
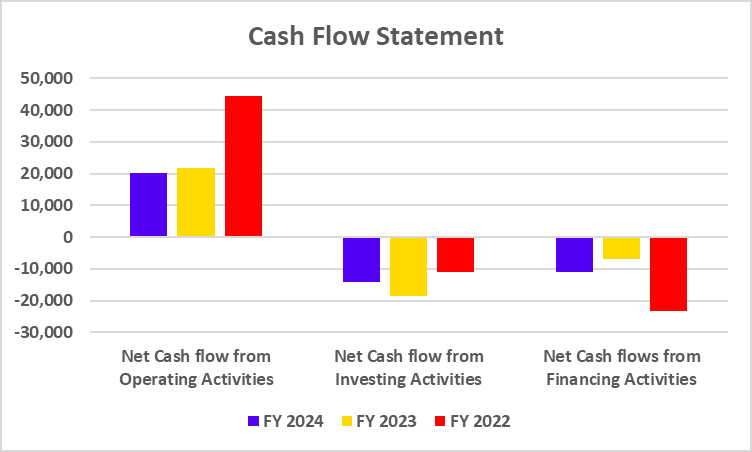
The company’s cash flow from operating activities showed a positive figure, which also exhibits a declining trend, and its cash flow from investing and financing activities showed negative figures.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
| Particulars | FY 2024 | FY 2023 | FY 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Margin (%) | 6.21 | 9.86 | 22.61 |
| Net Profit Margin (%) | -2.11 | 3.14 | 16.84 |
| ROCE (%) | 8.13 | 12.58 | 28.31 |
| Current Ratio | 0.72 | 0.89 | 1.02 |
| Return on Net Worth/Equity (%) | -4.82 | 8.49 | 35.08 |
| Debt to Equity Ratio | 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.60 |
The company’s net profit and operating profit margin have been on a declining trend for the last 3 years, and so has its return on capital employed.
Read Also: Tata Motors: Ordinary Shares vs DVR Shares
SWOT Analysis of Tata Steel
Tata Steel SWOT Analysis highlights its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the competitive steel industry:
Strengths
- Brand Image – The companies of the Tata Group are well-known in India. It helps them in attracting new customers.
- Broad Product Range– The company offers a wide variety of products, which helps it cater to multiple industries.
- Geographical Reach – The corporation can continue to rely on a steady income stream because of its presence in Europe and India.
- Product Pricing – The firm owns some of the mines, allowing it to control the expenses and prices of its products.
Weaknesses
- Cost of Acquisition – Tata Steel has made numerous domestic and international acquisitions, which will increase the company’s debt.
- Business Cycle – The steel industry is cyclical, and steel companies may not perform well during tough economic times.
- Prices of Commodities – Changes in commodity prices will directly impact the performance of this industry.
Opportunities
- Technological Advancement – The corporation will be able to lower production costs by integrating modern technologies into production processes.
- Strategic Partnership – The business can broaden its reach by forming more strategic alliances with foreign companies.
- Product Diversification – By adding specialized steel goods to its lineup, the corporation can broaden its product offering and increase sales.
Threat
- Competition – The price war between businesses will intensify due to the increased competition, which will lower the company’s profit margin.
- Global Demand – Any economic downturn will result in a decline in the demand for steel goods, which would affect the company’s revenue and profits.
- Environmental Concern – Due to the carbon-intensive nature of the steel-making process, the corporation must invest to lower its carbon footprint.
Read Also: JSW Steel Case Study: Business Model, Product Portfolio, and SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
Tata Steel has been a part of India’s business landscape for a century and is among the country’s oldest enterprises. The company is one of the world’s biggest steel producers, with operations worldwide. However, the company reported a net loss in the last financial year and also faces environmental concerns. However, one should consult a financial advisor before investing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who is the CEO of Tata Steel Limited?
Mr. Thachat Viswanath Narendran is the company’s current CEO and managing director.
Where are Tata Steel’s major plants located in India?
Tata Steel’s major plants are located in Jamshedpur and Kalinganagar.
Where is Tata Steel headquartered?
The headquarters of Tata Steel is situated in Mumbai.
Is Tata Steel a profitable company?
The company has reported a net loss of INR 4,851 crores for FY 2024. Along with this, the company’s revenue has also fallen.
What are the risks associated with investing in Tata Steel Shares?
The company reported a loss in FY 2024 and faces competition and environmental concerns, making investment in Tata Steel shares risky.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.