| Type | Description | Contributor | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post created | Pocketful Team | Jan-21-25 |
Risks in Commodity Trading and How to Manage Them

Commodity trading is the process of buying and selling commodities such as crude oil, gold, agricultural products, etc. Numerous trading opportunities emerge for traders every day, but unfortunately, risk also accompanies commodity trading. These risks arise from geopolitical and other economic factors, making this market very volatile and filled with high-risk-reward trading opportunities.
This blog focuses on the different risks involved and risk management in commodity trading. We will explain the major risks and describe the strategies to tackle them.
5 Key Risks in Commodity Trading
Commodity trading risks are the various risks that traders face while participating in the commodity market. These risks are determined by factors such as the supply-demand balance, general macroeconomic conditions, and sometimes the impact of unexpected events. Below are the most important risks, with examples cited and techniques on how to manage them.
1. Price Volatility Risk
What it is:
One of the greatest risks in commodity trading is price volatility. Commodities are extremely sensitive to supply and demand, political instability, weather conditions, or any other natural disasters.
Examples:
- A rise in crude oil prices was observed in 2022 when the war began between Ukraine and Russia.
- The price of wheat and many other commodities was high due to the drought affecting specific regions.
How to Manage:
- Set stop-loss orders in volatile market conditions.
- Diversify your trading positions across different commodities in order to minimize risk.
- Track the latest market trends and make quick trading decisions according to them.
2. Credit Risk
What it is:
Credit risk arises when a party in the commodity trading contract fails to meet his financial obligations. This occurs in OTC markets.
Examples:
- A buyer fails to make payment upon maturity of the forward contract.
- A counterparty defaults and is unable to deliver commodities as specified in the forward contract.
How to Manage:
- Engaging in regulated exchanges with clearinghouses that eliminate counterparty risks.
- Conduct due diligence before entering into contracts with counterparties.
- Security deposits or collateral agreements so that counterparty fulfills the contract obligations.
3. Geopolitical Risk
What it is:
Events such as wars, trade restrictions, and political instability can cause a disruption in the supply chain and dramatically influence commodity prices.
Examples
- Sanctions on Russian oil exports caused a global shortage of crude oil in 2022.
- China placed restrictions on the export of rare earth metals in 2023, which affected the semiconductor manufacturing companies that use them as raw materials.
How to Manage:
- Monitor recent news in the world to be able to anticipate any disruption beforehand.
- Use derivative instruments to fix prices and reduce uncertainty.
4. Leverage Risk
What it is:
Leverage enables the trader to create large positions with relatively small amounts of capital. Both profits and losses are magnified using leverage. Overuse of leverage can lead to huge losses.
Examples:
- A trader’s long position in gold futures with high leverage can result in huge losses if there is an unexpected drop in gold prices.
- High levels of leverage caught many retail traders off-guard when the price of oil crashed overnight in 2020.
How to manage:
- Limit the use of leverage by ensuring that position size is aligned with your level of risk tolerance.
- Maintain a sufficient balance in your trading account to avoid margin calls.
5. Liquidity Risk
What it is:
Liquidity risk occurs when not enough trading activity is happening in the commodities market. Without sufficient liquidity, creating a long or short position in a commodity can be challenging without affecting its price.
Examples:
- Commodities like lead and copper usually have lower liquidity than crude oil or gold.
- When the economy experiences a recession, market participation reduces, and liquidity worsens.
How to control:
- Trade in high-liquidity commodities such as crude oil, gold, and natural gas.
- Monitor the trading volumes and identify trading sessions during which market activity usually declines and avoid trading during that session.
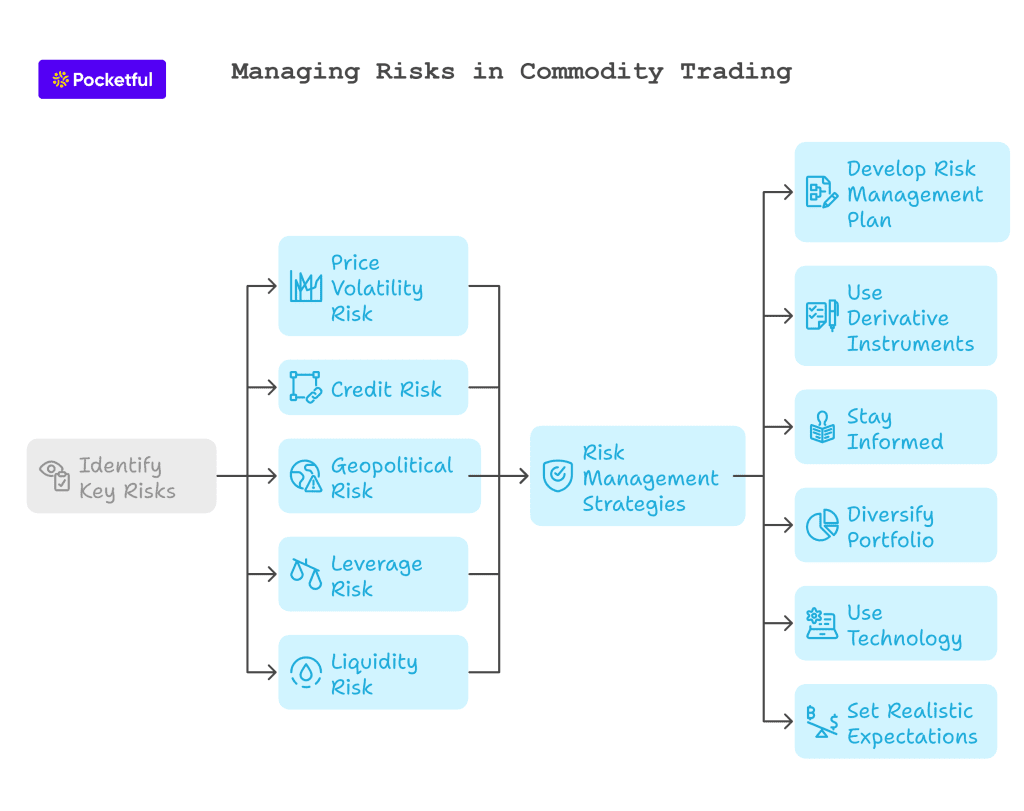
How to Effectively Manage Risks in Commodity Trading
Identifying the possible risks may be the first step, but a comprehensive risk management strategy provides you with a plan to mitigate these risks. Below are a few ways to manage the risks in commodity trading effectively:
- Developing a Risk Management Plan: Begin with a comprehensive plan that defines your risk tolerance, investment goals, and exit strategies.
- Derivative Instruments: Derivatives include futures, options, and swaps. Such instruments can be used to hedge the risks that exist in commodity trading.
- Stay Informed on Market Developments: Use real-time market data and news to anticipate future events and the associated risks. Most commodity trading platforms provide regular updates that help traders make the right decisions.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Allocate your trading capital across different commodity types so that you don’t suffer a huge loss due to unfavorable events affecting a particular commodity.
- Use Technology: The most advanced trading platforms have all these sophisticated tools, such as algorithmic trading bots, risk analytics, and automated alerts, which allow traders to make swift decisions and, thereby, reduce risks.
- Set Realistic Expectations: Don’t be tempted to overtrade and chase high returns. Consistent profits arise from disciplined trading and proper risk management.
Read Also: How to Trade in the Commodity Market?
Conclusion
Buying and selling commodities is considered risky, but you can master it with a disciplined approach to risk management and a well-defined trading strategy. Active risk management approach and advanced trading platforms can help you avoid major risks arising from price volatility, high leverage or geopolitical events. Before trading in commodities, one must make sure that one’s knowledge, trading strategy, and risk management system are in place in order to remain successful over the long term.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the most volatile commodities to trade?
Some of the most volatile commodities are crude oil, natural gas, and lead. Their prices can change sharply due to supply-demand imbalances, weather conditions, or geopolitical events.
How can I avoid losses due to leverage?
You can avoid losses due to leverage by creating conservative trading positions, maintaining sufficient margins, and having strict stop-loss levels to prevent significant drawdowns.
What is the best way to hedge in commodity markets?
The best way to hedge is by using derivative instruments such as futures and options.
Can I trade commodities with minimal risk?
No trade can be completely risk-free; however, you can definitely minimize risks by trading in highly liquid commodities, designing sophisticated risk management tools, and using leverage judiciously.
What is the role of diversification in commodity trading?
Diversifying the portfolio ensures the lowering of risk by spreading investments across many classes of commodities like energy, metals, and agriculture. If there is an adverse price change for a certain commodity, the rest can mitigate losses by performing well, ensuring effective risk management during volatile markets.
Disclaimer
The securities, funds, and strategies discussed in this blog are provided for informational purposes only. They do not represent endorsements or recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research and seek professional advice before making any investment decisions.